Order Reaction Rate Law Equation Feb 13 2023 nbsp 0183 32 Given the rate law equation text rate k A 1 B 2 nonumber 2 Determine a the reaction order with respect to A b the reaction order with respect to B and c the total
In chemistry the rate equation also known as the rate law or empirical differential rate equation is an empirical differential mathematical expression for the reaction rate of a given reaction in terms of concentrations of chemical species and constant parameters normally rate coefficients and partial orders of reaction only For many reactions the initial rate is given by a power law such as where and are the molar concentrations of the species and usually in moles per liter molarity Feb 13 2023 nbsp 0183 32 Either the differential rate law or the integrated rate law can be used to determine the reaction order from experimental data Often the exponents in the rate law are the positive
Order Reaction Rate Law Equation

Order Reaction Rate Law Equation
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/asTXZPlX_WM/maxresdefault.jpg
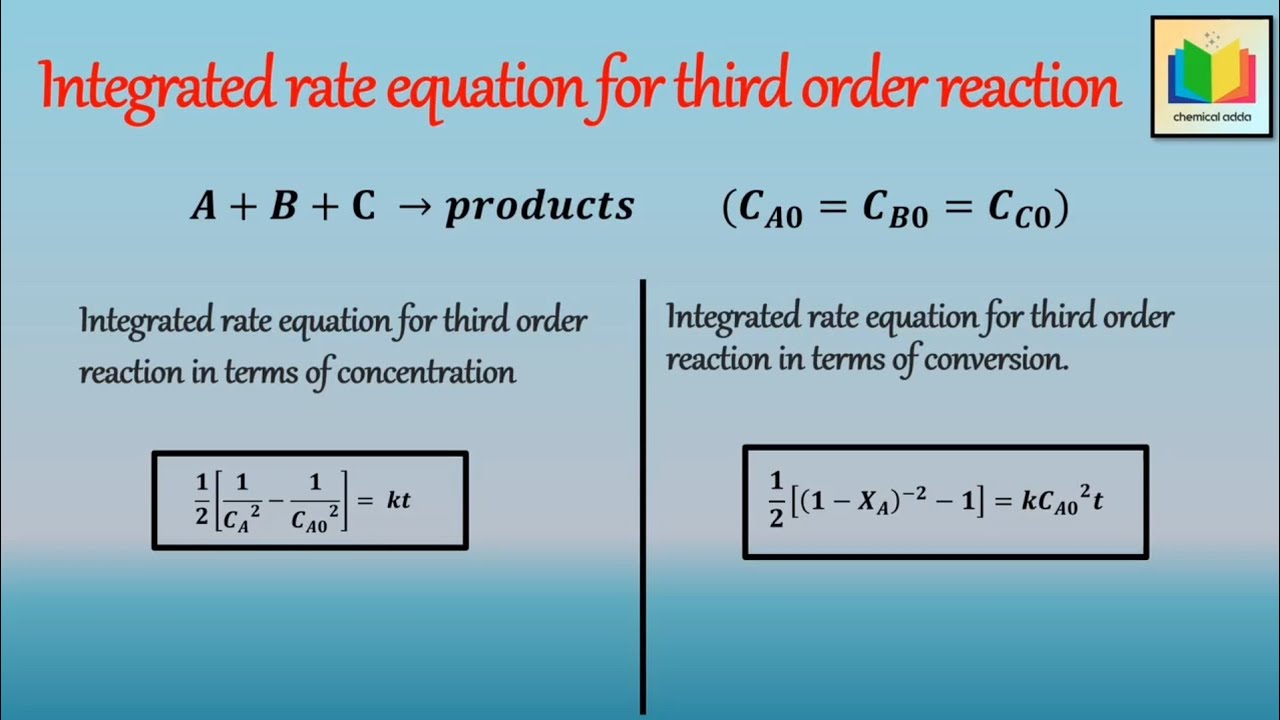
Integrated Rate Equation For Third Order Reaction Third Order
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/cgaaUtV0QqY/maxresdefault.jpg
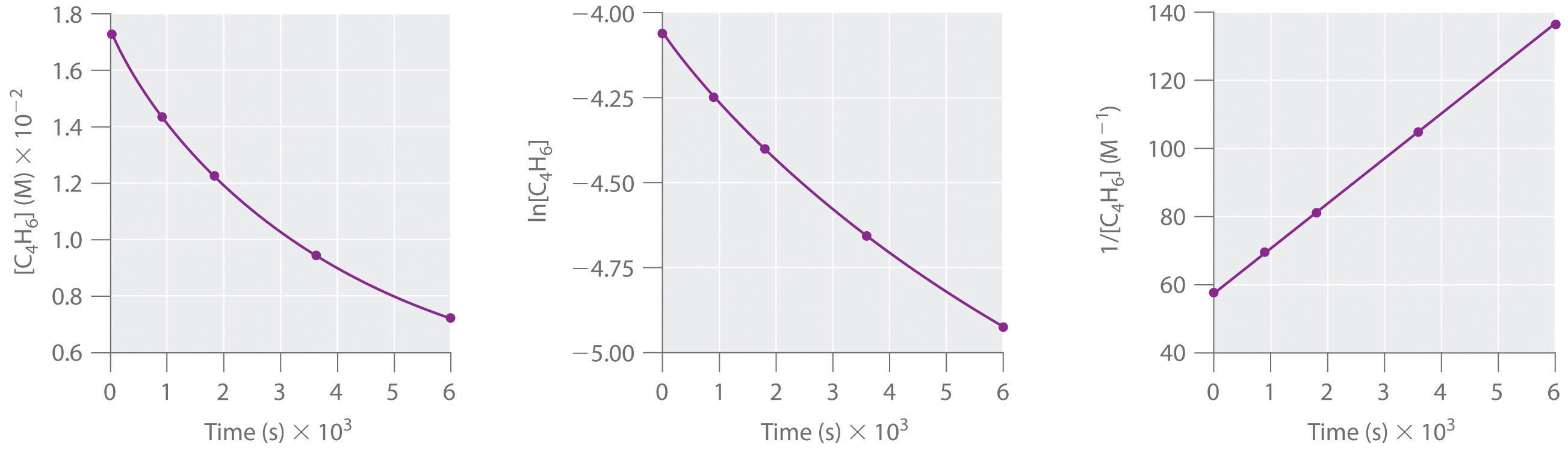
Using Graphs To Determine Rate Laws Rate Constants And Reaction Orders
http://saylordotorg.github.io/text_general-chemistry-principles-patterns-and-applications-v1.0/section_18/db20fbc24566c56823df39e68c74dd7f.jpg
The rate law for the reaction is determined to be rate k H 2 O 2 Fe 2 The rate constant at certain temperature is 2 56 x 10 24 M 183 s Calculate the rate of the reaction at this temperature if H 2 O 2 0 48 M and H 2 O 2 0 070 M Changing the concentration of substances taking part in a reaction usually changes the rate of the reaction A rate equation shows this effect mathematically Orders of reaction are a part of the rate equation This page introduces and
Determine the rate law and overall order for a chemical reaction using initial rate data Compare and contrast the effect of concentration or pressure on the rates of three common orders of reactions zero first and second order We need to know the rate law of a reaction in order to determine The order of the reaction with respect to one or more reactants The overall order of the reaction For the rate law Order with
More picture related to Order Reaction Rate Law Equation
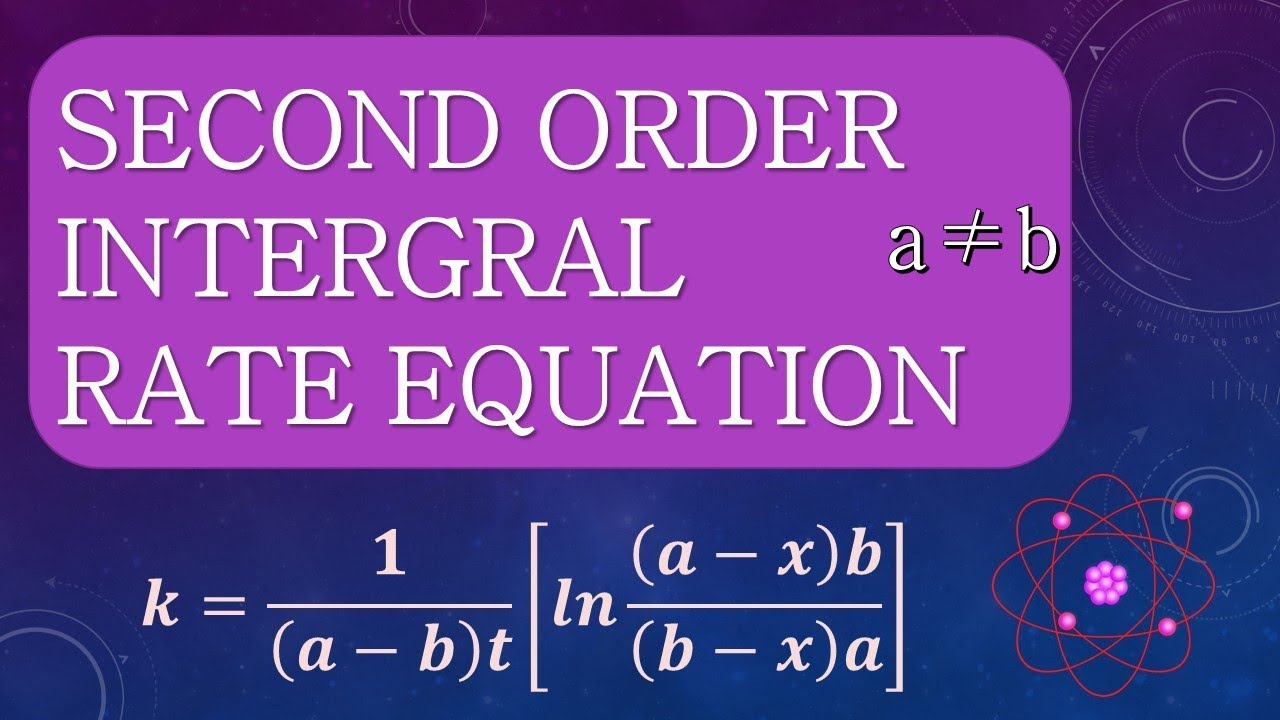
INTEGRATED RATE EQUATION FOR SECOND ORDER REACTION Where A b YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Ha45ESk8Qc0/maxresdefault.jpg

Rate Law And Reaction Order Kinetics AP Chemistry Khan Academy
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/6Ng8ayarWHw/maxresdefault.jpg
Rate Constant Equation Second Order Tessshebaylo
https://www.chem.fsu.edu/chemlab/chm1046course/Integrated.JPG
From the above rate law equation the order of reaction is x y Note that x and y are not stoichiometric coefficients The table below lists the values of x y for the different reaction orders The rate law is a mathematical relationship obtained by comparing reaction rates with reactant concentrations The reaction order is the sum of the concentration term exponents in a rate law
Rate laws or rate equations are mathematical expressions that describe the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentration of its reactants In general a rate law or differential rate law as it is sometimes If the rate law of a reaction is Rate k A 2 B the reaction is second order in A first order in B and third order overall The units of the rate constant k are M 2 s 1
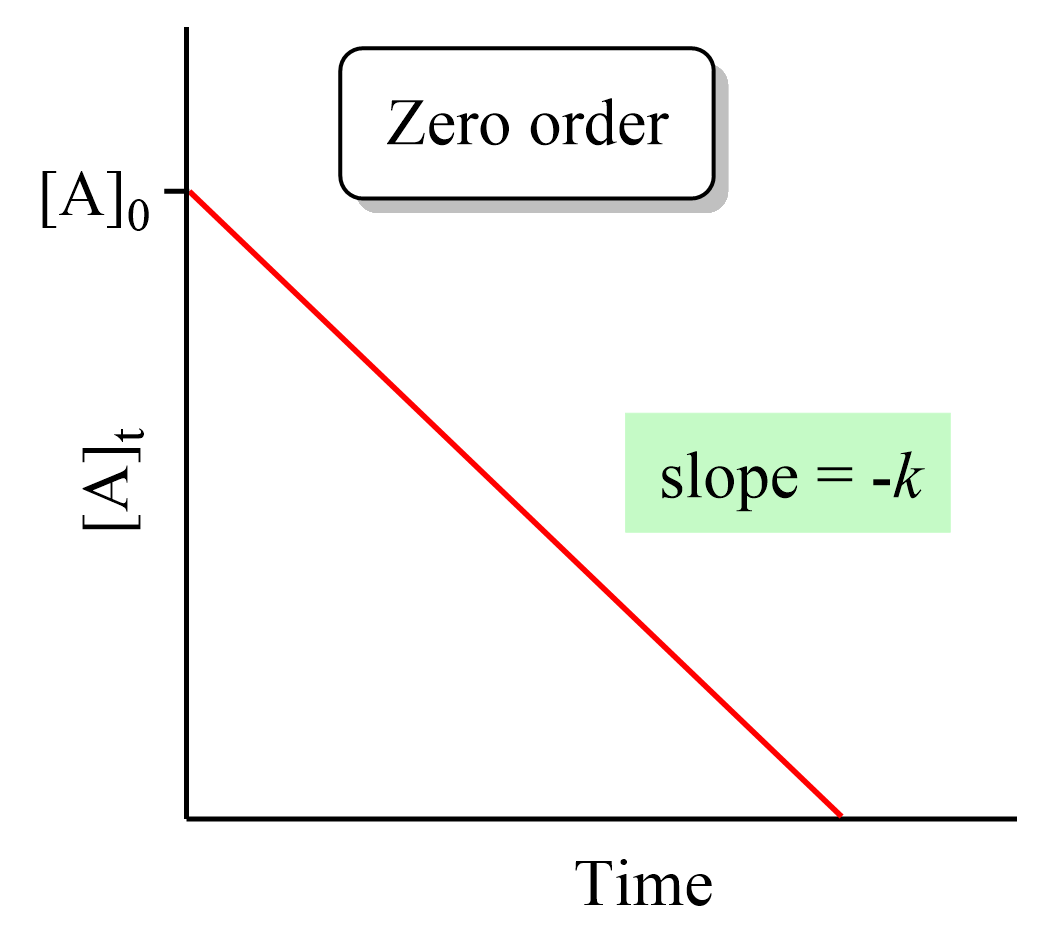
Zero Order Reactions Chemistry Steps
https://general.chemistrysteps.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Zero-order-rate-law-liner-equation-graph.png

Solved Derive The Rate Equation For A Reversible First order Chegg
https://d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net/media/07b/07b858ab-fe5f-415e-8d7f-0c1a8e9731e5/phpHFTu6w.png
Order Reaction Rate Law Equation - To determine the rate law from a table you must mathematically calculate how differences in molar concentrations of reactants affect the reaction rate to figure out the order of each