What 5 Factors Influence The Rate Of A Chemical Reaction Feb 7 2019 nbsp 0183 32 Some chemical reactions are nearly instantaneous while others usually take some time to reach the final equilibrium This article aims to help
Jun 19 2020 nbsp 0183 32 We can identify five factors that affect the rates of chemical reactions the chemical nature of the reacting substances the state of Apr 24 2017 nbsp 0183 32 Reaction rate is controlled by multiple factors all of which can be varied under controlled conditions In almost very case raising the temperature of chemicals increases the
What 5 Factors Influence The Rate Of A Chemical Reaction

What 5 Factors Influence The Rate Of A Chemical Reaction
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/-4HXaUBbv04/maxresdefault.jpg
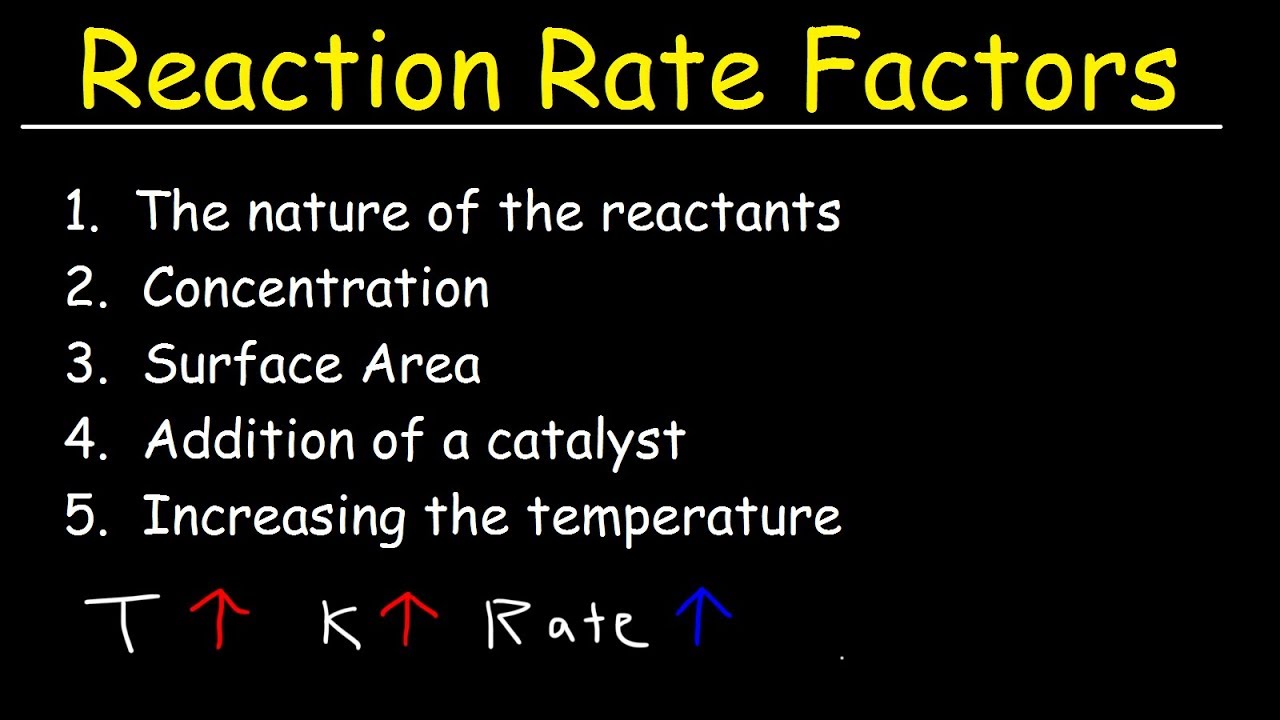
Factors Affecting The Rate Of The Reaction Chemical Kinetics YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/JpoOfrPKgmM/maxresdefault.jpg

Chapter 17A General Chemistry Mr Mata Ppt Download
https://slideplayer.com/slide/15256875/92/images/3/Essential+Question:+What+factors+influence+the+reaction+rate+of+a+chemical+reaction.jpg
FACTORS AFFECTING RATE OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS The rate of a chemical reaction is affected by several factors like 1 Concentration of reactants 2 Pressure 3 Temperature 4 Catalyst 5 Nature of reactants 6 Orientation Nov 26 2019 nbsp 0183 32 Several factors can influence the chemical reaction rate In general a factor that increases the number of collisions between particles will increase the reaction rate and a factor that decreases the number of collisions
The speed of a chemical reaction is affected by temperature concentration particle size and the presence of a catalyst It can be calculated by measuring changes in reactants products We can identify five factors that affect the rates of chemical reactions the chemical nature of the reacting substances the state of subdivision one large lump versus many small particles of
More picture related to What 5 Factors Influence The Rate Of A Chemical Reaction

Making Reactions Faster Factors Affecting Rates Of Reaction Gcse
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/3b/20/e5/3b20e5abe274b06f9ac7fddf018be47d.png

Factors Affecting Reaction Rates YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/NZIvtJCVcDo/maxresdefault.jpg
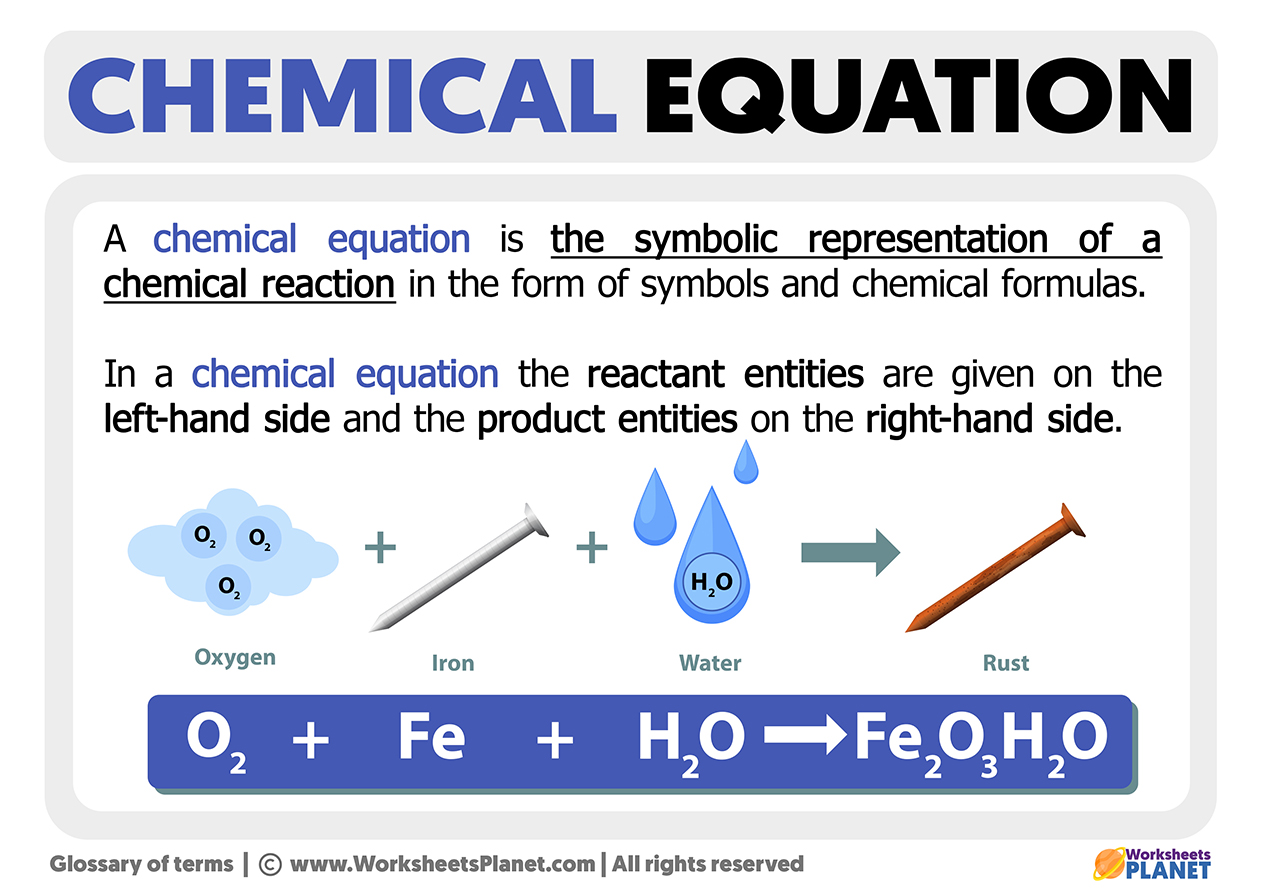
What Is A Chemical Equation
https://www.worksheetsplanet.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/What-is-a-chemical-equation.jpg
Nov 20 2024 nbsp 0183 32 Increasing the concentration of a solution or gas pressure increases the rate of reaction Increasing the temperature increases the rate of reaction Increasing the surface area increases the rate of reaction Surface Five factors typically affecting the rates of chemical reactions will be explored in this section the chemical nature of the reacting substances the state of subdivision one large lump versus
May 25 2021 nbsp 0183 32 Chemists have identified many factors that affect the rate of a reaction The rate or speed at which a reaction occurs depends on the frequency of successful collisions Feb 16 2020 nbsp 0183 32 The rate of reaction is affected by reactant concentration temperature pressure surface area of the particles phase effects and catalysts Chemical reactions take place when
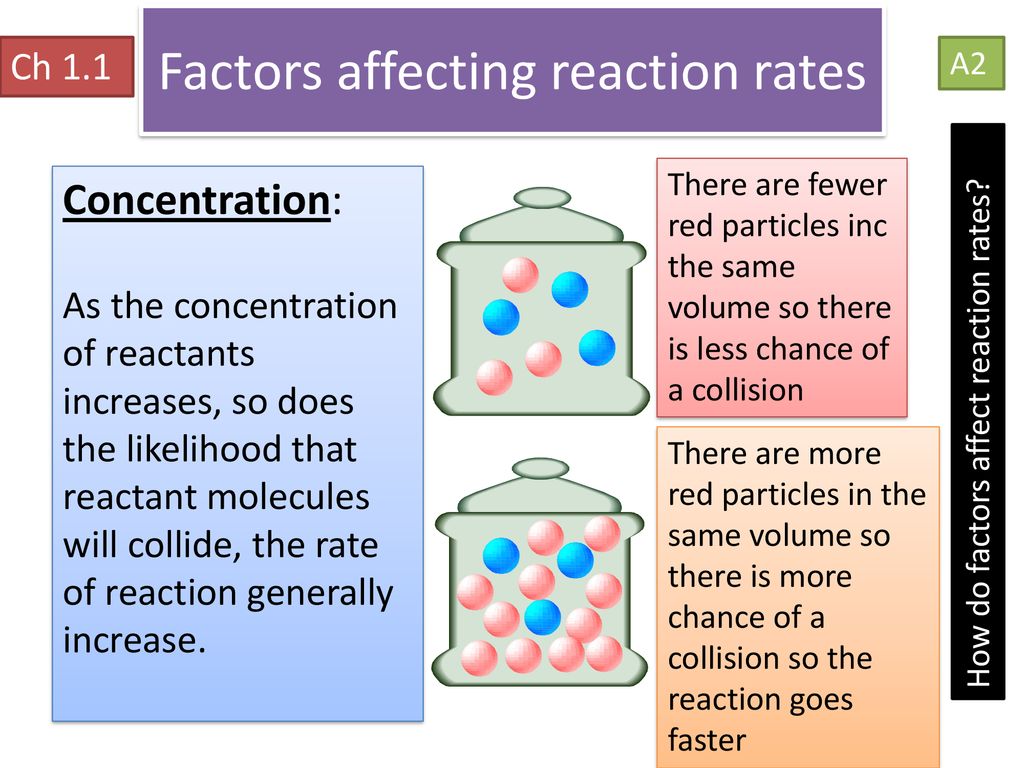
Chapter 1 Rate Of Reaction Ppt Download
https://slideplayer.com/slide/15098838/91/images/6/Factors+affecting+reaction+rates.jpg
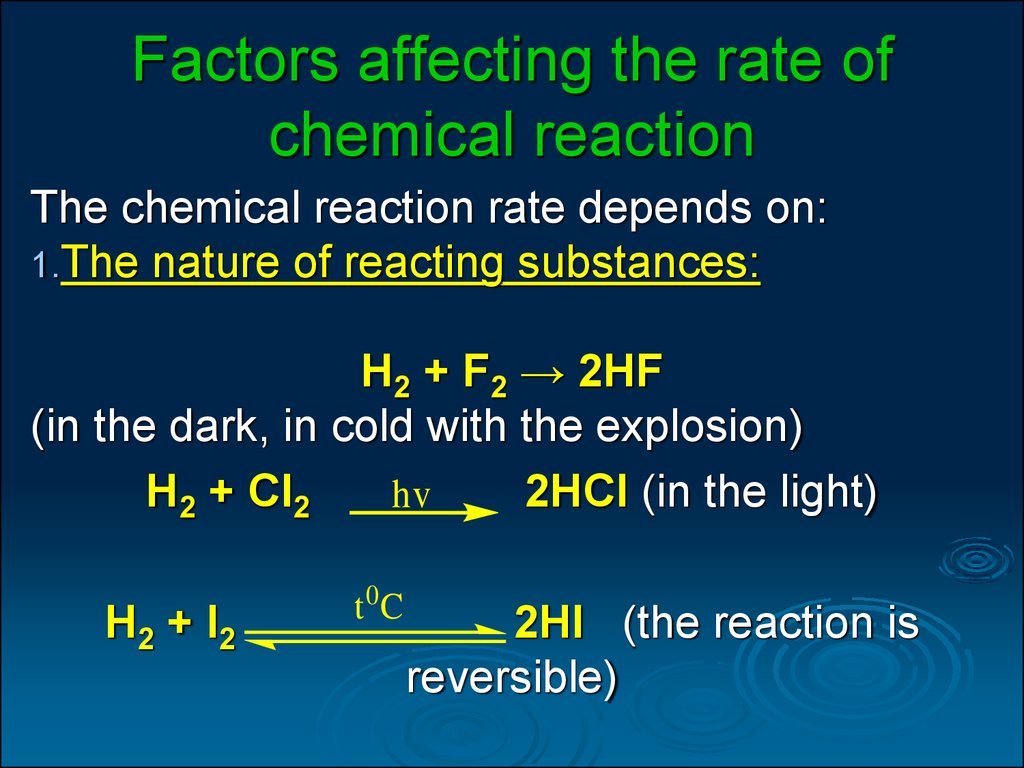
Factors Affecting The Rate Of Chemical Reaction
https://cf.ppt-online.org/files/slide/i/ISHfNCBKgTAkQn452mvbL1PshMxJzjtcya7EdZ/slide-2.jpg
What 5 Factors Influence The Rate Of A Chemical Reaction - The speed of a chemical reaction is affected by temperature concentration particle size and the presence of a catalyst It can be calculated by measuring changes in reactants products