Enzyme Activation Energy Graph Explained Master Enzyme Activation Energy with free video lessons step by step explanations practice problems examples and FAQs Learn from expert tutors and get exam ready
Sep 5 2021 nbsp 0183 32 Enzymes lower the activation energy needed for chemical reactions allowing them to occur faster The graph shows that reactions without enzymes have a high activation energy first curve while those with enzymes have a significantly lower activation energy second curve Feb 13 2023 nbsp 0183 32 The activation energy E a labeled Delta G ddagger in Figure 2 is the energy difference between the reactants and the activated complex also known as transition state In a chemical reaction the transition state is defined as the highest energy state of
Enzyme Activation Energy Graph Explained
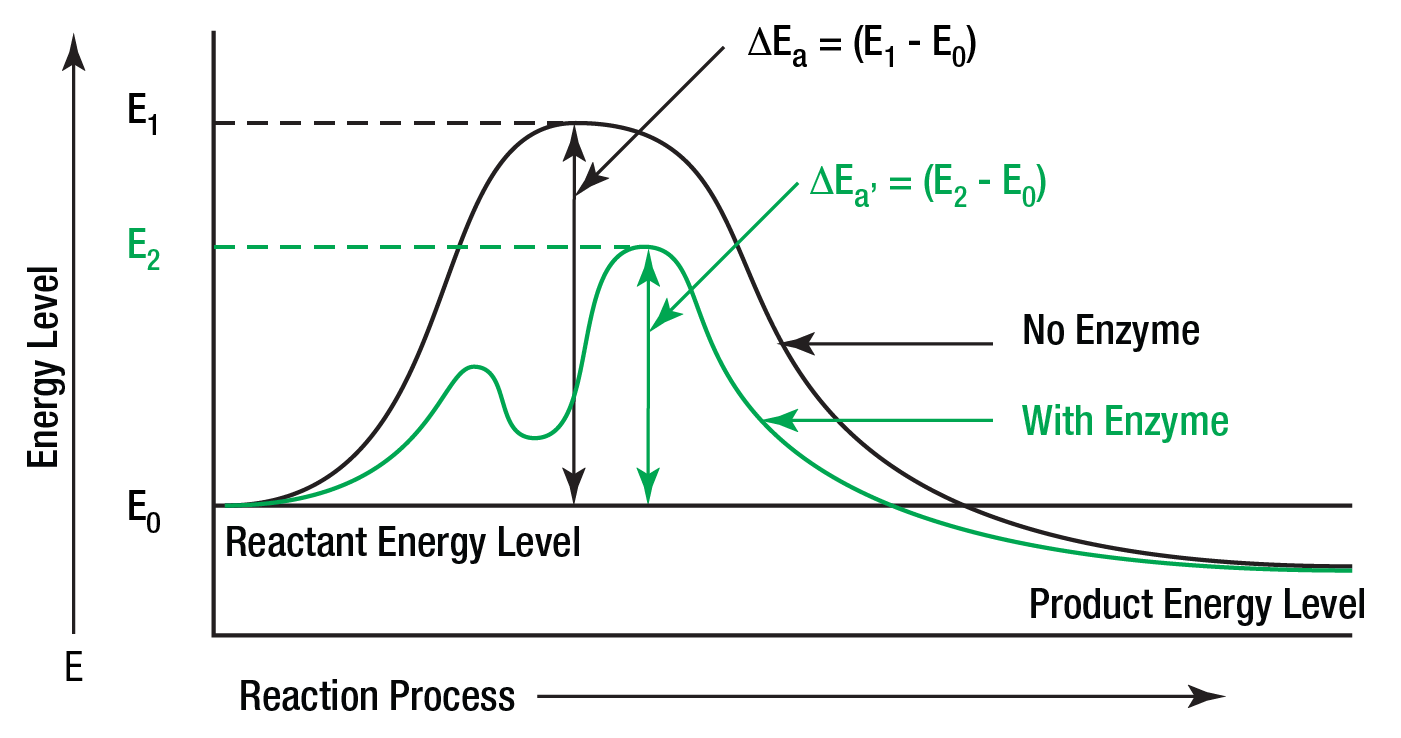
Enzyme Activation Energy Graph Explained
https://www.worthington-biochem.com/sites/default/files/inline-images/Enzyme_Figure-3.png

Catalyst Effect On Energy Diagram CHEMISTRY COMMUNITY
https://i.stack.imgur.com/NIBao.jpg

Transition state Theory Definition Facts Britannica
https://cdn.britannica.com/28/4728-050-C4ABAC20/activation-energy-equation-Arrhenius-reactants-products-reaction.jpg
Figure 1 Enzymes lower the activation energy of the reaction but do not change the free energy of the reaction Here the solid line in the graph shows the energy required for reactants to turn into products without a catalyst The dotted line shows the energy required using a catalyst What is activation energy It is the nrg necessary to get the reaction to go forward even if it is an exergonic reaction What is activation energy or blue line coincides with the point where the bonds in the reactants of the reaction are weakest It is also called a transition state
Jul 18 2014 nbsp 0183 32 The difference in the activation energy of substrate and product is indicated on the graph If P is at a lower level than S then the reaction is an exothermic reaction The difference in average energy content of S from that of its transition state is called activation energy The activation energy is the energy difference between reactant and transition state The activation energy of a reaction is usually denoted by Ea and given in units of kilojoules per mole kJ mol or Kilocalories per moles Kcal mol and is defined as
More picture related to Enzyme Activation Energy Graph Explained

12 Using Graph 1 Explain How Enzymes Work Include The Term
https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/d06/e8e08178bb5976526a2c71a44aa57084.png
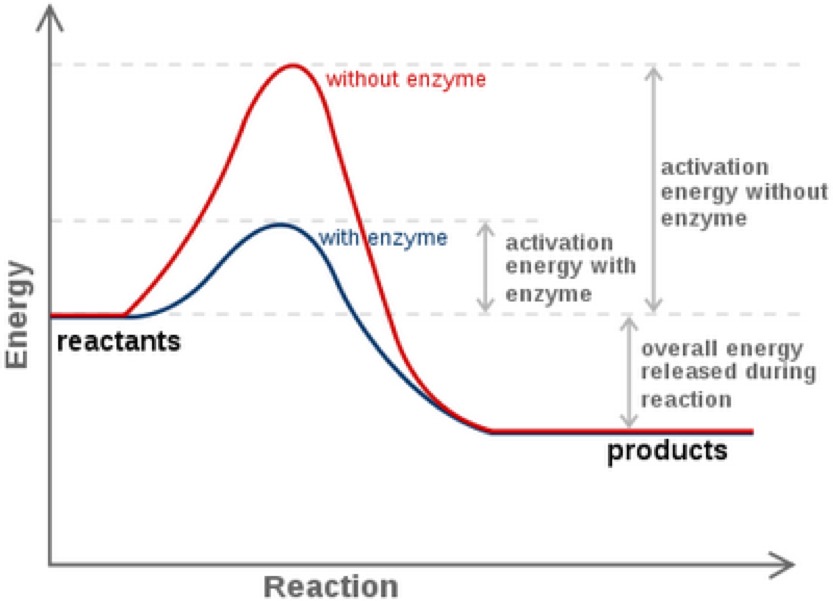
Enzymes And Reaction Rates
http://www2.nau.edu/lrm22/lessons/enzymes/reaction.png

Question Video Identifying The Activation Energy Of An Enzyme
https://media.nagwa.com/790171073053/en/thumbnail_l.jpeg
In chemistry activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required for a chemical reaction The activation energy can be thought of as the magnitude of a potential barrier that the reacting molecules need to overcome to initiate a reaction and convert into products A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by reducing the amount of energy needed to start that reaction This is called lowering the activation energy
Feb 26 2022 nbsp 0183 32 The free energy graph can be used to determine whether the reaction will be spontaneous or not by evaluating the G G can be found by subtracting the free energy of the reactants from the free energy of the products Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions IB Topic 2 5 We know that they have an active site where the substrate binds and that when a substrate collides with an active site then a reaction occurs The reason that enzymes speed up these reactions

Methane Combustion Equation Balanced Tessshebaylo
http://media.opencurriculum.org/articles_manual/ck12_biology/chemical-reactions/3.png

Pin On Nursing Physiology
https://i.pinimg.com/736x/61/aa/42/61aa424cd3e81756f14a4a7e0e2c32b0.jpg
Enzyme Activation Energy Graph Explained - Be able to explain why there is an optimum temperature including discussion of the activation energy speed of reaction high temperatures structurally denature the enzyme protein Be able to interpret and discuss graphs of enzyme reaction rate versus temperature and deducing the optimum temperature for a particular enzyme reaction