Elastic Collision Problems Worksheet With Answers Elastic Collision Problems and Solutions Post a Comment Problem 1 A 0 015 kg marble moving to the right at 0 225 m s makes an elastic head on collision with a 0 030 kg shooter marble moving to the left at 0 180 m s After the collision the smaller marble moves to the left at 0 315 m s Assume that neither marble rotates before or after the
Now to solve problems involving one dimensional elastic collisions between two objects we can use the equation for conservation of momentum First the equation for conservation of momentum for two objects in a one dimensional collision is p1 p2 p 1 p 2 Fnet 0 p 1 p 2 p 1 p 2 F net 0 Elastic collision Answer b Elastic collision Explanation The total kinetic energy is conserved in an elastic collision 5 State true or false In an elastic collision momentum is not conserved TRUE FALSE Answer b FALSE Explanation In an elastic collision momentum is not conserved
Elastic Collision Problems Worksheet With Answers
Elastic Collision Problems Worksheet With Answers
https://i2.wp.com/media.cheggcdn.com/media/507/5076a688-a413-4d17-9e41-fe96e7175f51/phpy2cLRp
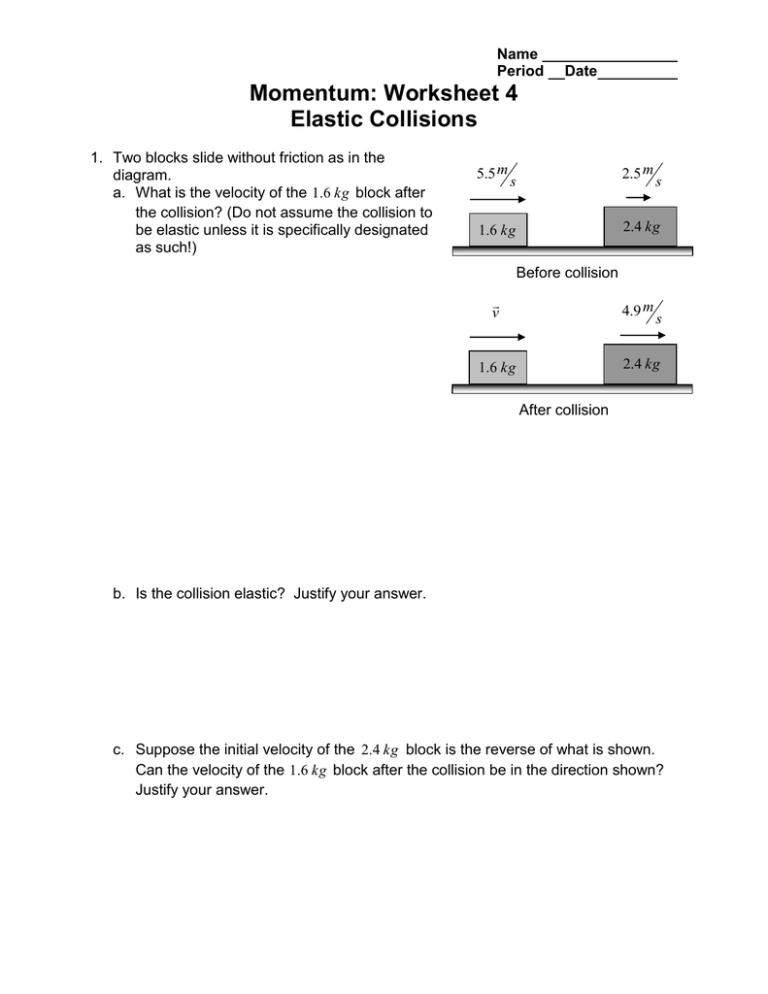
Momentum Worksheet 4 Elastic Collisions
https://s2.studylib.net/store/data/012116253_1-94547ba1b8998d9bc4bef708eec757a8-768x994.png

Elastic Collision Worksheet Physics Elastic Collisions Worksheet
https://i1.wp.com/media.cheggcdn.com/media/144/144ff3a0-e381-4371-b248-f209c08ebff0/phppnhZB8.png
Elastic and Inelastic Collisions Worksheet total momentum before total momentum after Show all work and circle your final answer mv A 10 kg ball rolling a speed of 20 m s strikes an 8 kg ball at rest The 10 kg ball comes to a rest and the 8 kg ball begins to roll forward Determine the 8 kg ball s velocity You are playing marbles Your 0 10 kg shooter traveling at 1 m s hits a stationary 0 05 kg cat s eye marble If it is an elastic collision what are the velocities after the collision A ballistic pendulum can be used to determine the muzzle velocity of a gun A 01 kg bullet is fired into a 3 kg block of wood
Elastic Collision Problems v 2 0 188 m s Example 9 A 112 g billiard ball moving at 1 54 m s strikes a second The additional problems can elastic or inelastic The answers are provided in your packet Collision Problems Example 11 A 98 kg fullback is running along at 8 6 m s when a 76 kg 2 PRACTICE PROBLEM Two marbles collide head on in an elastic collision Marble A has a mass of 14 g and is initially moving to the right at 2 5 m s while Marble B has a mass of 12 g and is initially moving to the left at 3 2 m s Assume that motion to the right is considered positive and motion to the left is considered negative
More picture related to Elastic Collision Problems Worksheet With Answers
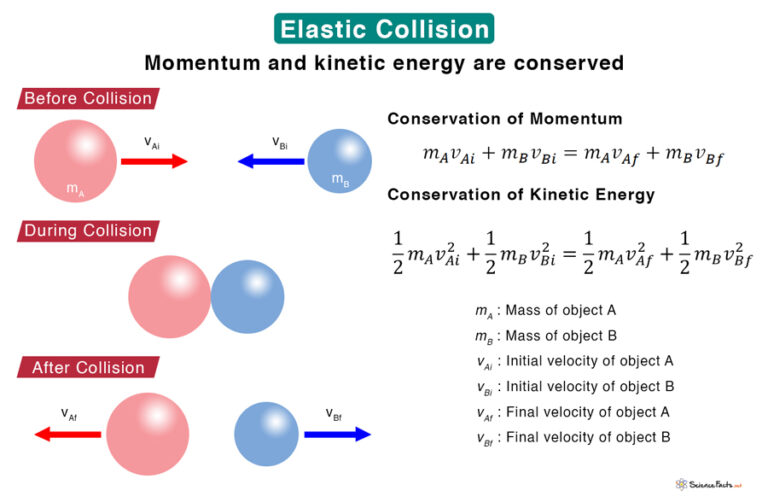
Elastic Collision Definition Formula And Examples
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Elastic-Collision-768x502.jpg
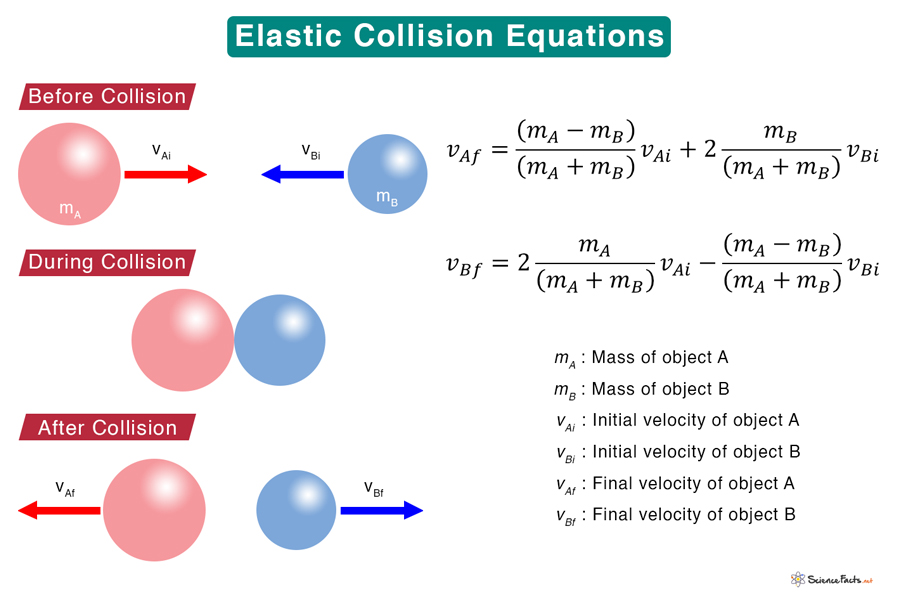
Elastic Collision Definition Formula And Examples
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Elastic-Collision-Formula.jpg
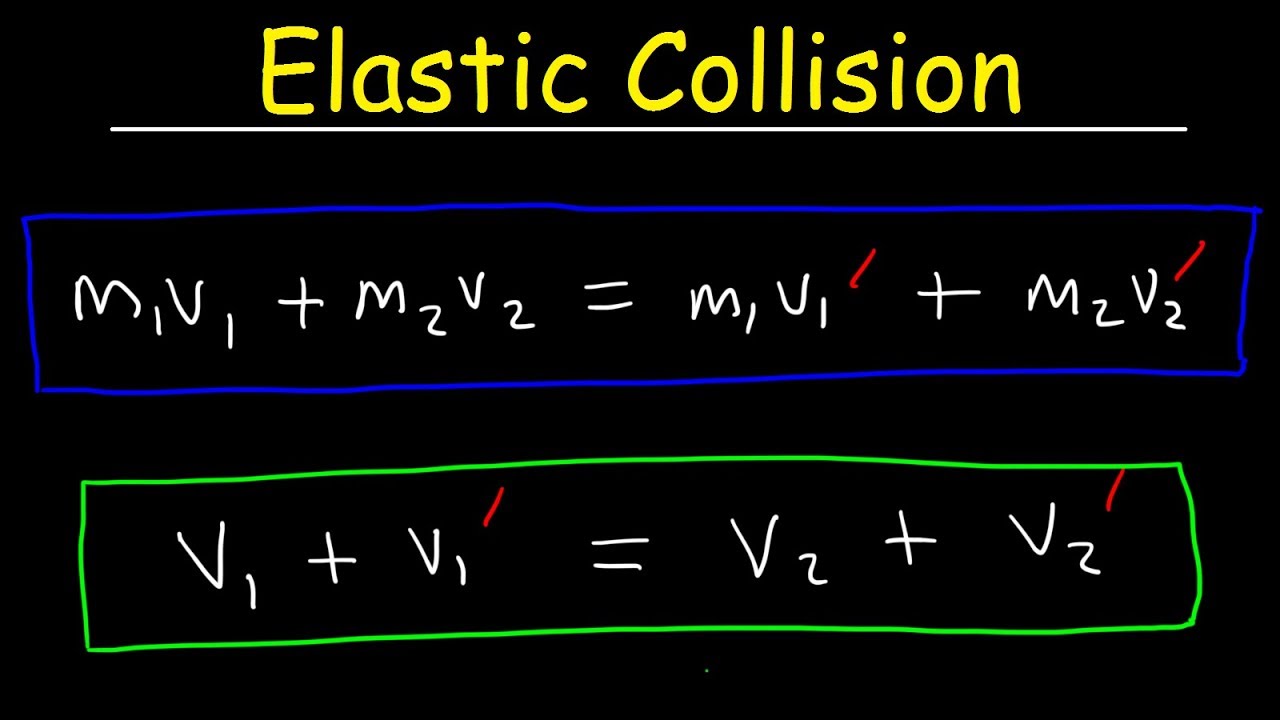
Elastic Collisions In One Dimension Physics Problems Conservation Of
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/CFbo_nBdBco/maxresdefault.jpg
To this activity you leave monitor an elastic collisions by move an ice cube into another ice cube on a smooth surface that that a minimal amount of energy is converted into heat Cash Elastic and Inelastic Collisions Worksheet Elastic and Inelastic Collisions answers Momentum Places Trial Package solutions Momentum AP First the equation for conservation of momentum for two objects in a one dimensional collision is p 1 p 2 p 1 p 2 F net 0 8 33 or m 1 v 1 m 2 v 2 m 1 v 1 m 2 v 2 F net 0 8 34 where the primes indicate values after the collision By definition an elastic collision conserves internal kinetic energy and
8 4 Elastic Collisions in One Dimension 50 Two identical objects such as billiard balls have a one dimensional collision in which one is initially motionless After the collision the moving object is stationary and the other moves with the same speed as the other originally had Show that both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved 51 Polly Ester and Ray Ahn are doing the Elastic Collision lab on a low friction track Cart A has a mass of 1 00 kg and is moving rightward at 27 6 cm s prior to the collision with Cart B Cart B has a mass of 0 50 kg and is moving leftward with a speed of 42 9 cm s After the magnetic repulsion of the two carts Cart A is moving leftward at 10 1
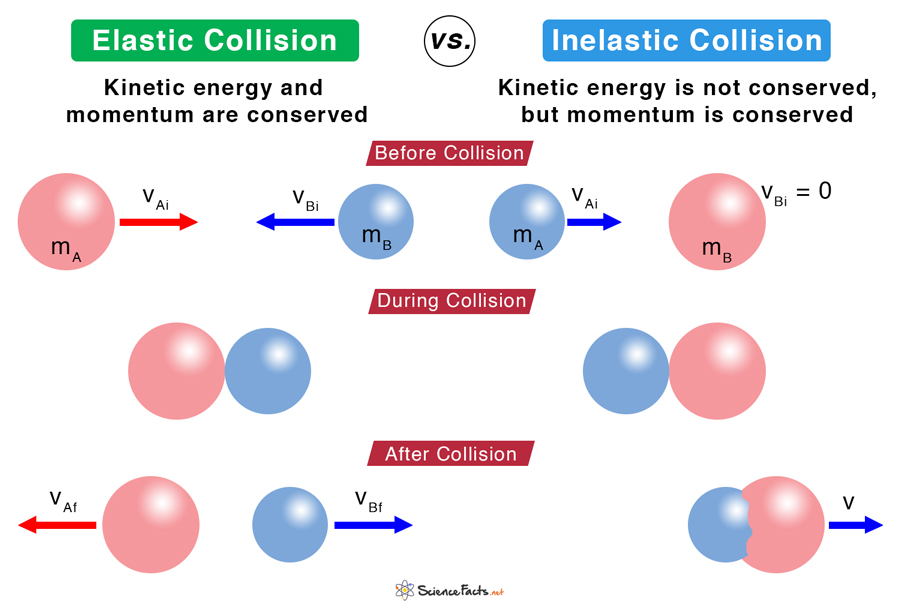
Inelastic Collision Definition Formula And Examples
https://www.sciencefacts.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Elastic-vs-Inelastic-Collision.jpg

Deriving The Equation For Perfect Elastic Collisions YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/4JbMqFJBhdg/maxresdefault.jpg
Elastic Collision Problems Worksheet With Answers - In this collision the two objects will bounce off each other While this is not technically an elastic collision it is more elastic than the previous collisions in which the two objects stick together A 3000 kg truck moving with a velocity of 10 m s hits a 1000 kg parked car The impact causes the 1000 kg car to be set in motion at 15 m s
