What Is Law Of Conservation Of Mass Explain With Example The law of conservation of mass is a scientific law popularized and systematized by the 18th century French chemist Antoine Lavoisier According to the law in an isolated system matter cannot be created or destroyed only changed
The law of conservation of mass states that in a chemical reaction between any object the mass that is produced by them is neither created nor destroyed The carbon atom changes from a complex solid structure to a simple gas but yet its mass remains the same Jun 3 2024 nbsp 0183 32 According to the law of conservation of mass mass is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction For example when coal is burned the carbon atom in it changes into carbon dioxide The carbon atom changes from a solid to a gas yet its mass remains constant
What Is Law Of Conservation Of Mass Explain With Example

What Is Law Of Conservation Of Mass Explain With Example
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/qqk04MeZsTU/maxresdefault.jpg
.jpg)
Law Of Conservation Of Mass Equation
https://slideplayer.com/slide/9210095/27/images/6/Law+of+Conservation+of+Mass-Example+(Figure+2.20+p148).jpg

Law Of Conservation Of Mass
https://sciencenotes.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Law-of-Conservation-of-Mass.png
Dec 9 2023 nbsp 0183 32 The Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental concept in chemistry stating that mass in an isolated system is neither created nor destroyed by chemical reactions or physical transformations According to the law the mass of the reactants in a chemical reaction equals the mass of the products When hydrogen gas burns and combines with oxygen to form water the mass of the water formed is equal to the mass of the hydrogen and oxygen consumed Thus this is in accordance with the law of conservation of mass
Like the conservation of energy there is a law of conservation of mass as well Read on to find some useful information regarding the same in the article mentioned below Nature is made up of various living and non living things and all these together form the mass of the Earth The total mass of chemicals before and after a reaction remains the same This is called the Law of Conservation of Mass
More picture related to What Is Law Of Conservation Of Mass Explain With Example

The Law Of Conservation Of Mass YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/0M-qNevHD-s/maxresdefault.jpg
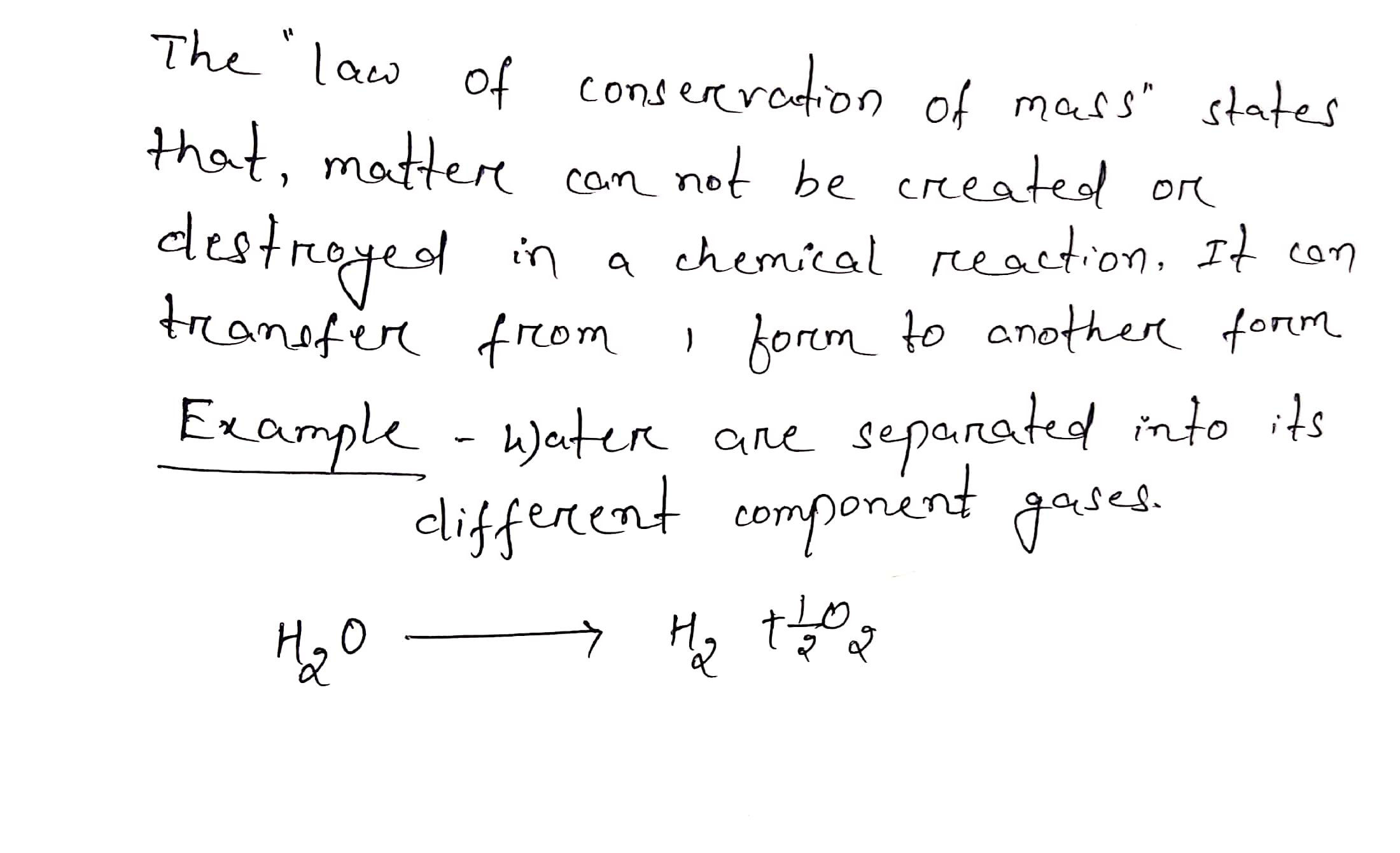
Explain Law Of Conservation Of Mass With Example
https://d1hj4to4g9ba46.cloudfront.net/questions/1397640_1232743_ans_ec949ee12848458dbce180d31eae20ee.jpg
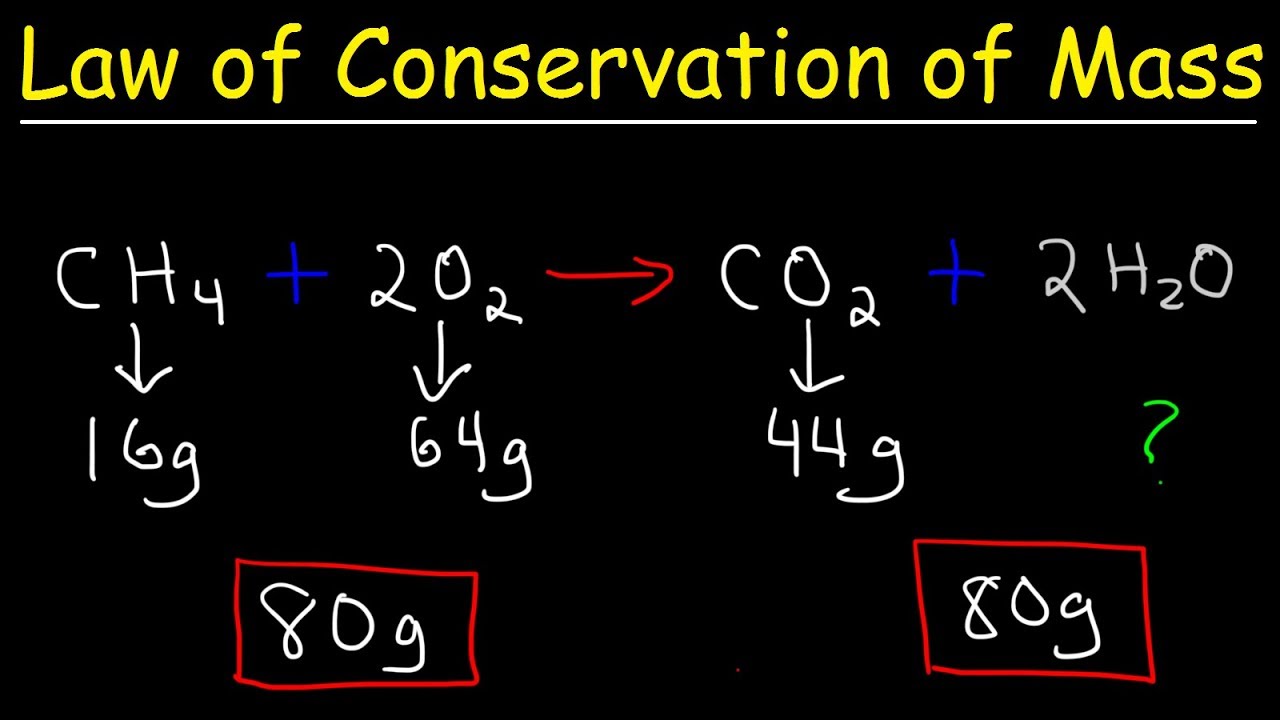
Law Of Conservation Of Mass Fundamental Chemical Laws Chemistry
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/eBTNzScLUg4/maxresdefault.jpg
In physics and chemistry the law of conservation of mass or principle of mass conservation states that for any system closed to all transfers of matter the mass of the system must remain constant over time Jul 17 2024 nbsp 0183 32 What is Law of Conservation of Mass The Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental concept in physics and chemistry stating that in an isolated system is neither created nor destroyed by chemical reactions or physical transformations
Dec 21 2020 nbsp 0183 32 The law of conservation of mass states that in a closed system including the whole universe mass can neither be created nor destroyed by chemical or physical changes In other words total mass is always conserved Dec 16 2024 nbsp 0183 32 During a chemical reaction the sum of the masses of the reactants and products remain unchanged This is known as the Law of Conservation of Mass As per this law Matter can never be created nor destroyed Total Mass of Reactants Total Mass of Products

The Law Of Conservation Of Matter Exploring Its Fundamental
https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:1024/1*LuSnZ5pOYx0hTxztMrSfVA.png
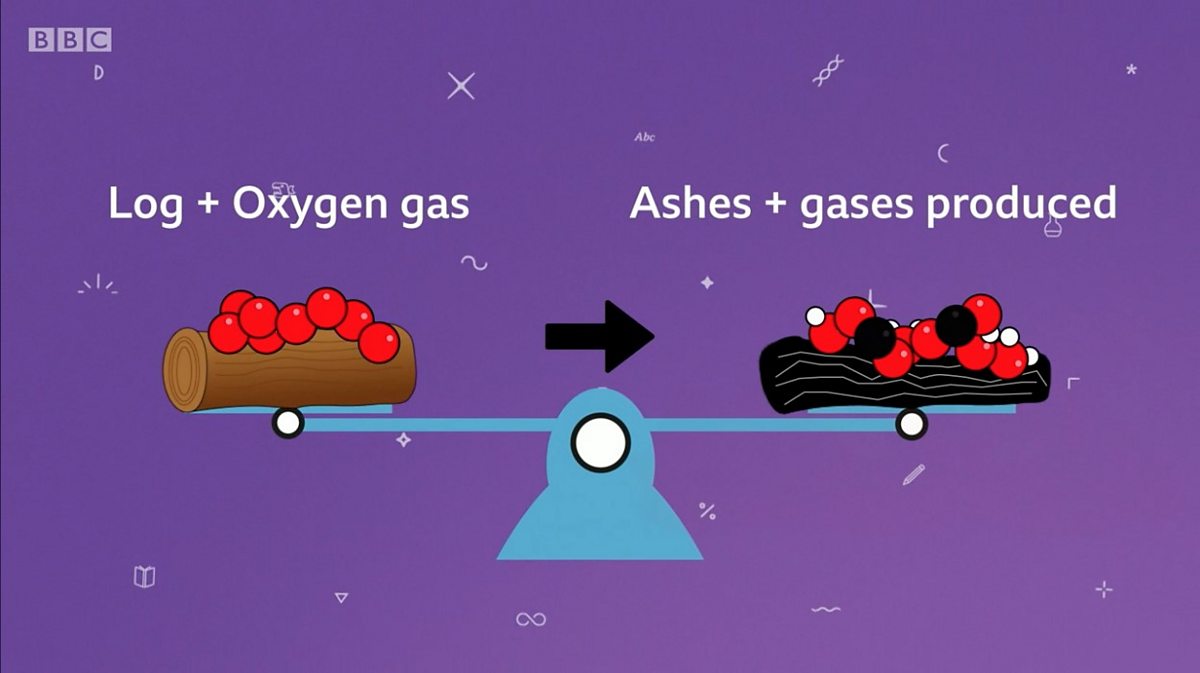
Law Of Conservation Of Mass Examples For Kids
https://ichef.bbci.co.uk/images/ic/1200xn/p09pjwrd.jpg
What Is Law Of Conservation Of Mass Explain With Example - Like the conservation of energy there is a law of conservation of mass as well Read on to find some useful information regarding the same in the article mentioned below Nature is made up of various living and non living things and all these together form the mass of the Earth