What Is Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Matter What is the Particle Theory of Matter The particle theory of matter or the kinetic molecular theory of matter describes the microscopic properties of atoms or molecules and their interactions which result in observable macroscopic properties such as pressure volume and temperature
Sep 21 2022 nbsp 0183 32 The kinetic molecular theory explains the states of matter and is based on the idea that matter is composed of tiny particles that are always in motion This theory helps explain observable properties and behaviors of solids liquids and gases Jan 30 2023 nbsp 0183 32 To understand the five fundamentals of Kinetic Molecular Theory To use Kinetic Molecular Theory to describe the behavior of the macroscopic gas laws
What Is Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Matter

What Is Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Matter
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/xBBpIWawwBI/maxresdefault.jpg

Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Gases Practice Problems YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/iAsP-9m2aH0/maxresdefault.jpg
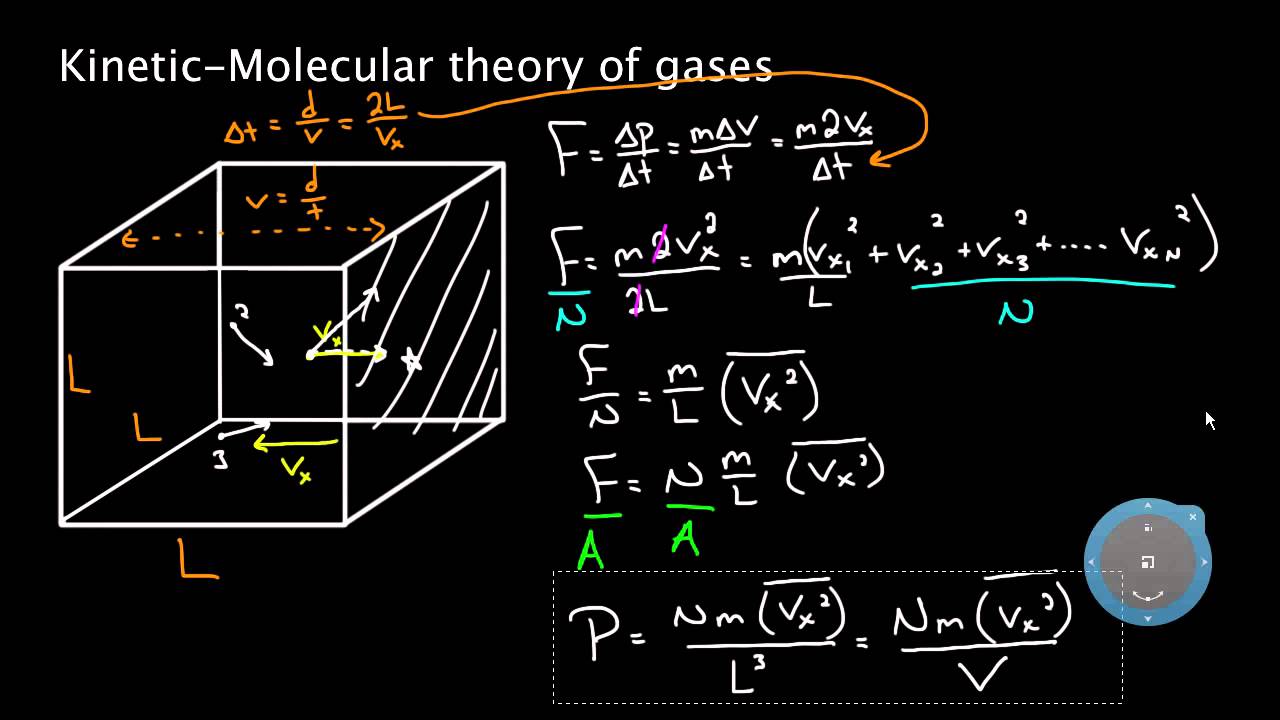
Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Gases Physical Processes MCAT Khan
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Qsa4aAdpHfY/maxresdefault.jpg
Jun 19 2020 nbsp 0183 32 The kinetic molecular theory is a theory that explains the states of matter and is based on the idea that matter is composed of tiny particles that are always in motion The theory helps explain observable properties and behaviors of solids liquids and gases The kinetic molecular theory is a scientific model that helps us understand the physical properties of matter such as solids liquids and gases and how they change from one state to another
The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Matter is a concept that basically states that matter is composed of a very large number of very tiny particles molecules or ions These particles are constantly in motion and possess energy of motion kinetic energy that we perceive as temperature The kinetic molecular theory is a simple but very effective model that effectively explains ideal gas behavior The theory assumes that gases consist of widely separated molecules of negligible volume that are in constant motion colliding elastically with one another and the walls of their container with average velocities determined by their
More picture related to What Is Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Matter
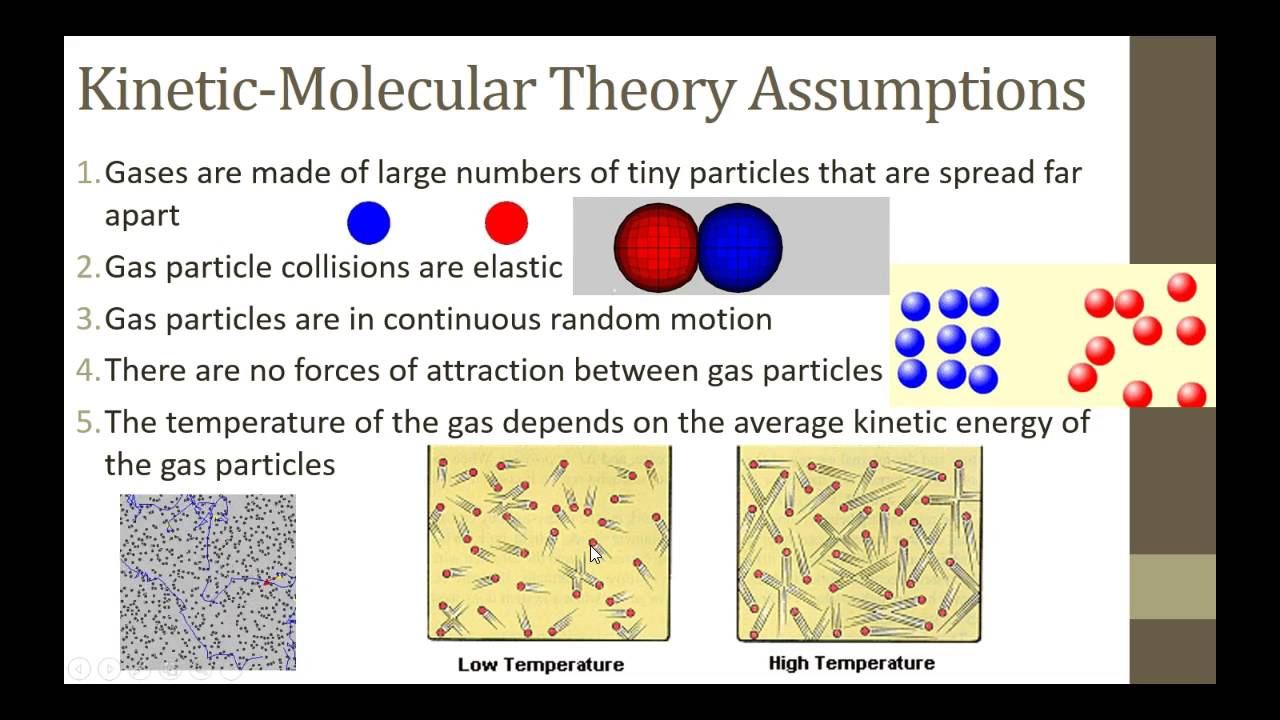
ChemB 10 1 Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Matter YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/V7LgfTwY5pk/maxresdefault.jpg
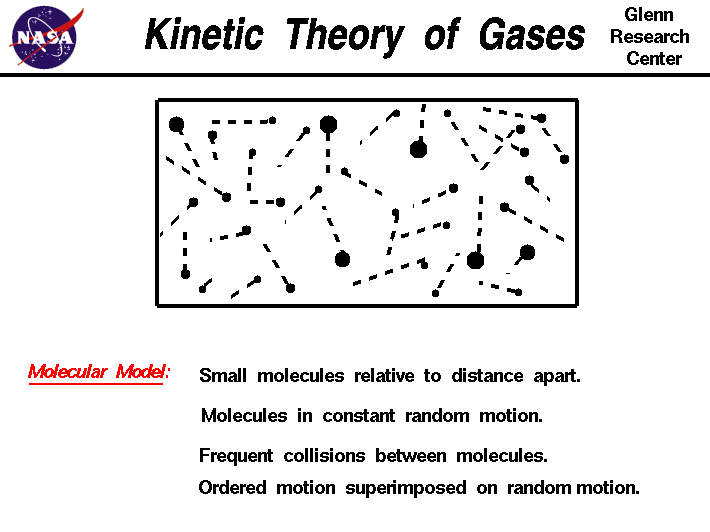
Kinetic Theory Of Gases
https://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/BGH/Images/kinth.gif

Kinetic Molecular Theory And Gases Ppt Download
https://slideplayer.com/slide/15515636/93/images/1/Kinetic+Molecular+Theory+and+Gases.jpg
The kinetic molecular theory KMT is a simple microscopic model that effectively explains the gas laws described in previous modules of this chapter This theory is based on the following five postulates described here The kinetic molecular theory of matter offers a description of the microscopic properties of atoms or molecules and their interactions leading to observable macroscopic properties such as pressure volume temperature
What is Kinetic Molecular Theory Kinetic Molecular Theory is a model that attempts to explain what happens in terms of groups of atoms and molecules colliding with each other and how those collisions change their energy levels as well as their physical and chemical properties 3 2 The kinetic molecular theory ESAAL The kinetic theory of matter helps us to explain why matter exists in different phases i e solid liquid and gas and how matter can change from one phase to another The kinetic theory of matter also helps

Pin Auf Amazing Facts Of Science Chemie
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/82/c3/9e/82c39e514541adcfb46e056e5ecf382f.jpg

1 Kinetic Molecular Theory YouTube
http://i.ytimg.com/vi/x-NQlNqMcNU/maxresdefault.jpg
What Is Kinetic Molecular Theory Of Matter - The kinetic molecular theory is a simple but very effective model that effectively explains ideal gas behavior The theory assumes that gases consist of widely separated molecules of negligible volume that are in constant motion colliding elastically with one another and the walls of their container with average velocities determined by their