What Is Initial Rate In Chem Jan 4 2025 nbsp 0183 32 Learn about the initial rates method for your A level chemistry exam This revision note includes information on concentration time graphs and tangents
Sep 22 2021 nbsp 0183 32 The method of initial rates allows the values of these reaction orders to be found by running the reaction multiple times under controlled conditions and measuring the rate of the reaction in each case Mar 1 2020 nbsp 0183 32 The initial rate of reaction is the instantaneous rate at the start of the reaction when t 0 In this case the unit for average instantaneous and initial rate of reaction is M s In most cases the reaction rate is dependent on the concentration of the various reactants at time t
What Is Initial Rate In Chem

What Is Initial Rate In Chem
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/G95rpHiUJhY/maxresdefault.jpg

A Level Biology How To Calculate Enzyme Rates YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/tQtdcq-caMg/maxresdefault.jpg

Gen Chem II 1 Solution Concentrations Conversions YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Rd-pkbJq5qg/maxresdefault.jpg
The method of initial rates involves measuring the initial rate of a chemical reaction for different initial concentrations of reactants By observing how the rate changes as the concentrations of the reactants change one can determine the reaction order with respect to each reactant The initial rate of a reaction is the instantaneous rate at the start of the reaction i e when t 0 The initial rate is equal to the negative of the slope of the curve of reactant concentration versus time at t 0
The Method of Initial Rates is a fundamental approach in chemical kinetics that allows researchers to investigate the relationship between concentration and reaction rate at the very onset of a reaction The initial rate r 0 is the rate of reaction at time t 0 In the Method of Initial Rates the differential rate law is determined by varying the initial concentrations of the various reactants and observing the effect on the initial rate
More picture related to What Is Initial Rate In Chem
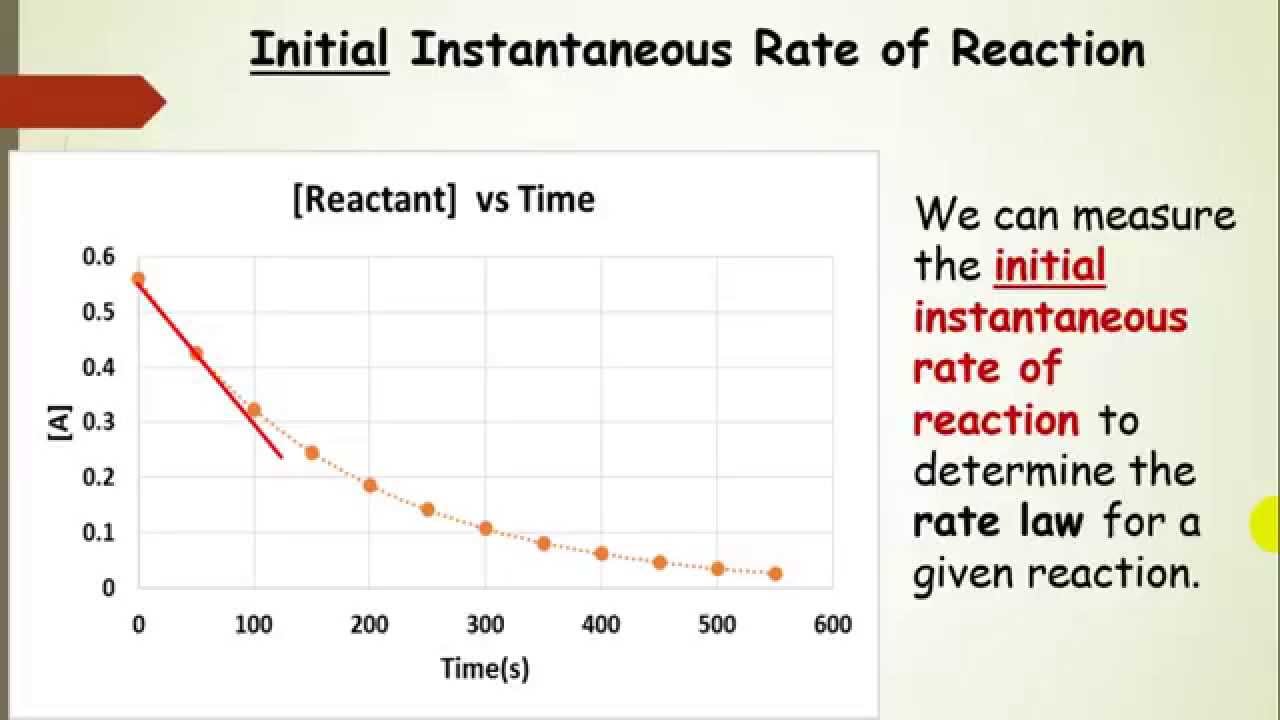
Finding The Rate Law Using Method Of Initial Rates Experiments
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/XO0ehBqv9hs/maxresdefault.jpg

Rate Of Change And Initial Value Of Graphs Instructional Video YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ChVLJRzPPZo/maxresdefault.jpg
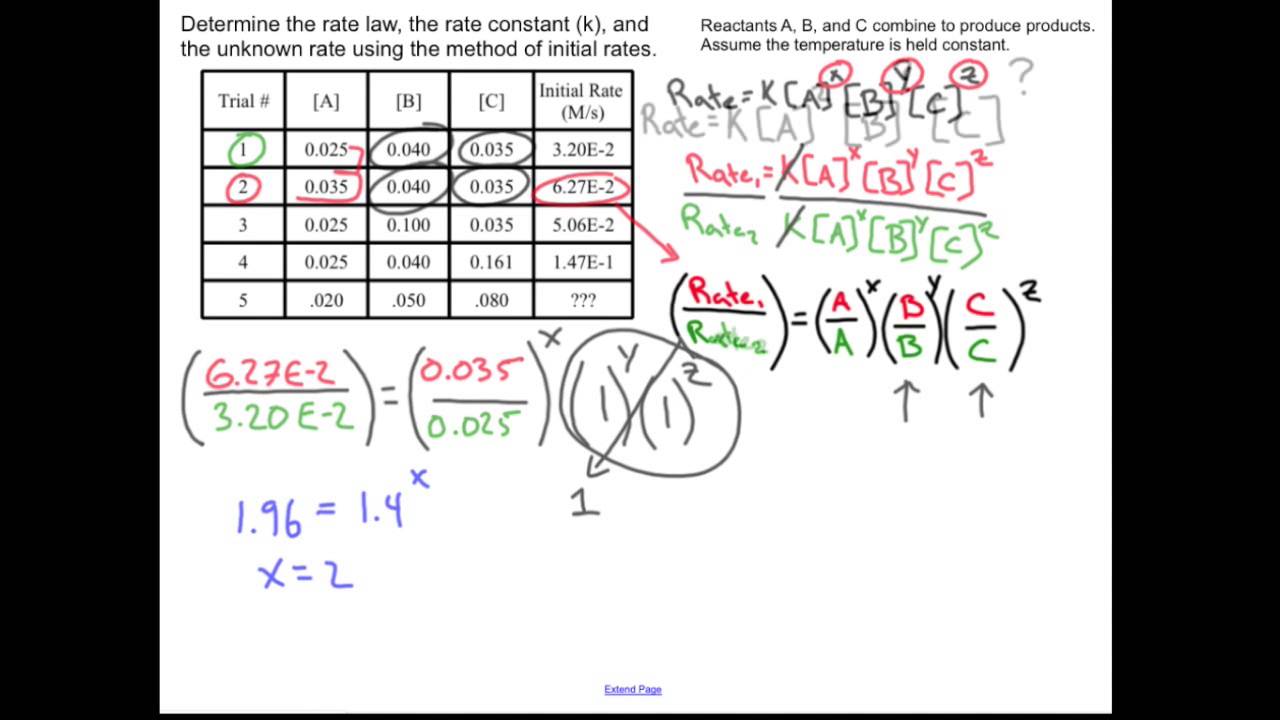
Rate Law And The Method Of Initial Rates Chemistry Sample Problem
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/IiYO_9sS7fI/maxresdefault.jpg
A common experimental approach to the determination of rate laws is the method of initial rates This method involves measuring reaction rates for multiple experimental trials carried out using different initial reactant concentrations In simple words we can say the initial rate is the rate at the very beginning of a reaction Complete answer We can say that the instantaneous rate at the start of the reaction that is when t 0 is called as Initial rate
The initial mass of the reacting mixture is measured and at the same time a stop clock is started A catalyst is a substance which increases the rate of a chemical reaction but it is not used The Method of Initial Rates is Used to Find the Order of Each Reactant the Overall Order of the Reaction and the Value of the Rate Constant for a Rate Law
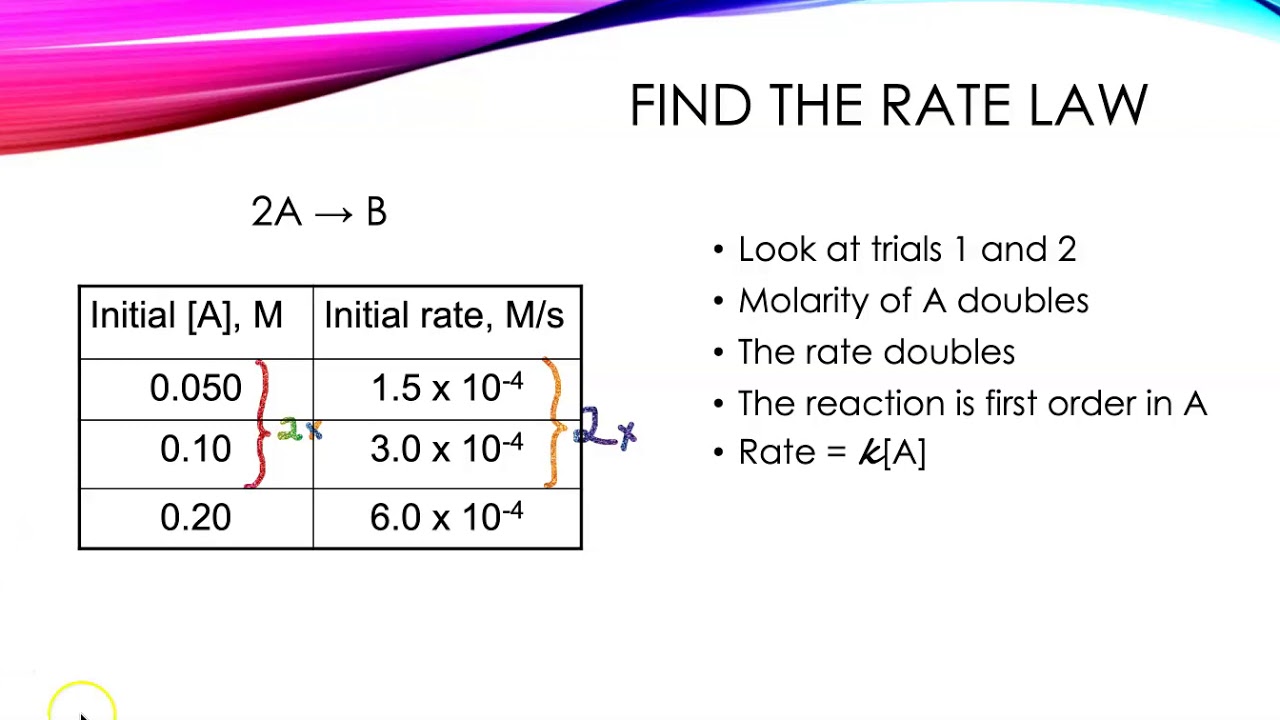
Rate Laws And The Method Of Initial Rates YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/m8vQk9zw6WA/maxresdefault.jpg

Initial Rate Method How To Calculate Order Of Reactions Using Initial
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/L8XAcBIea5g/maxresdefault.jpg
What Is Initial Rate In Chem - The initial rate of a reaction is the instantaneous rate at the start of the reaction i e when t 0 The initial rate is equal to the negative of the slope of the curve of reactant concentration versus time at t 0