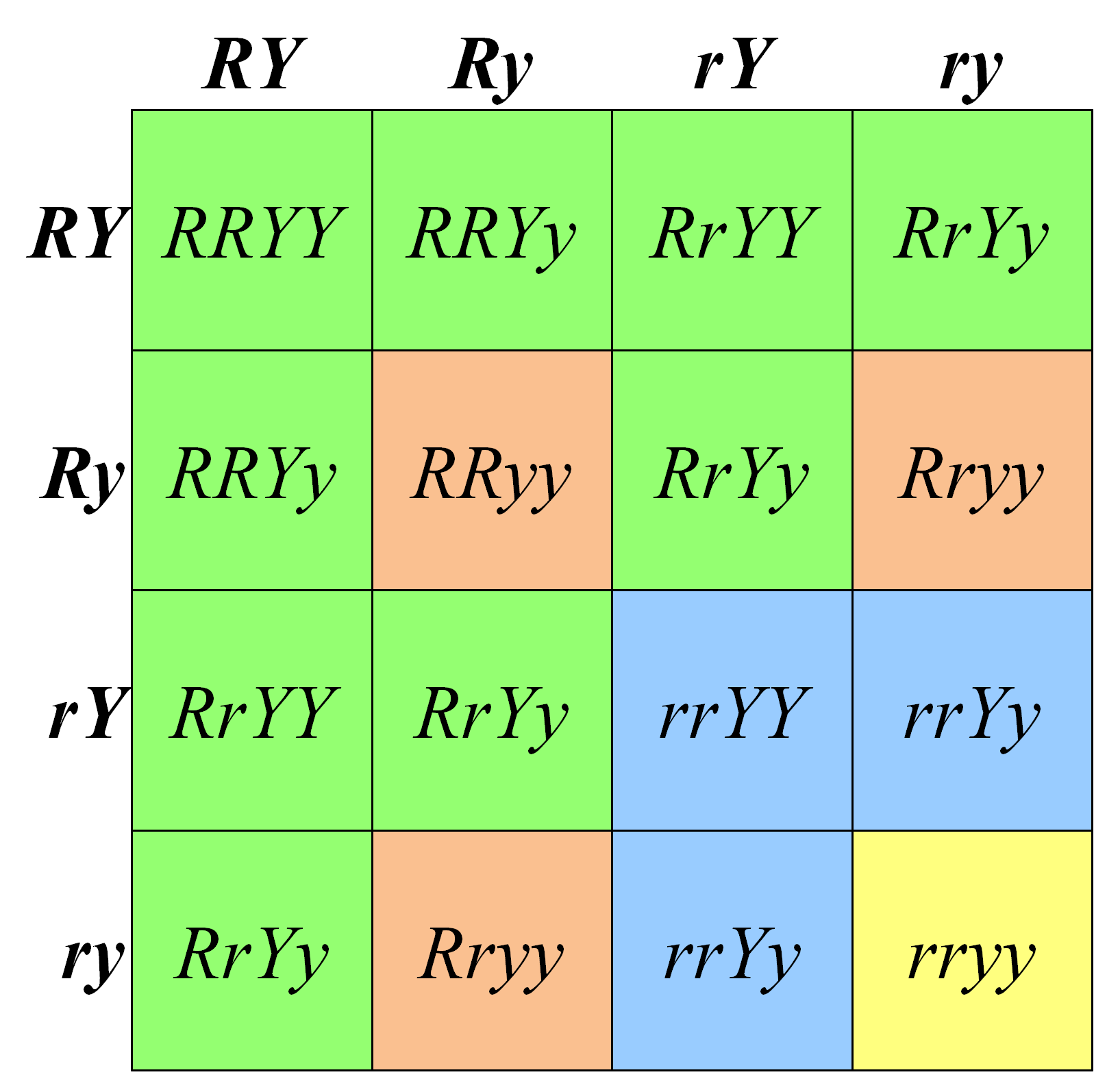
The Phenotypic Ratios Of Monohybrid And Dihybrid Crosses Are Altered By Mar 11 2025 nbsp 0183 32 The 9 3 3 1 and 1 1 1 1 ratios emerge in dihybrid inheritance where two genes each with dominant and recessive alleles segregate independently Mendel first described these patterns in pea plant experiments crossing individuals heterozygous for
By applying the product rule to all combinations of phenotypes we can predict a 9 3 3 1 phenotypic ratio among the progeny of a dihybrid cross if certain conditions are met including the independent segregation of the alleles at each locus Jan 21 2018 nbsp 0183 32 The key difference between monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross is that in a monohybrid cross inheritance of one trait e g height is studied while in a dihybrid cross inheritance of two independent traits e g flower colour stem length is studied
The Phenotypic Ratios Of Monohybrid And Dihybrid Crosses Are Altered By
The Phenotypic Ratios Of Monohybrid And Dihybrid Crosses Are Altered By
https://useruploads.socratic.org/ETUSa9nNRm6UW9tDuzRG_88E99755-4231-4252-A2D7-BAF33EAA3F89.png
/monohybrid_cross-58d567715f9b5846830d0d91.jpg)
Monohybrid Cross A Genetics Definition
https://fthmb.tqn.com/9qCPgjHvRQZN1SaT9RaY4HuKh7Y=/1500x1000/filters:fill(auto,1)/monohybrid_cross-58d567715f9b5846830d0d91.jpg
Genotypic Ratio Definition Calculation And 3 Examples
https://microbenotes.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Genotypic-Ratio-in-Monohybrid-Cross.jpg
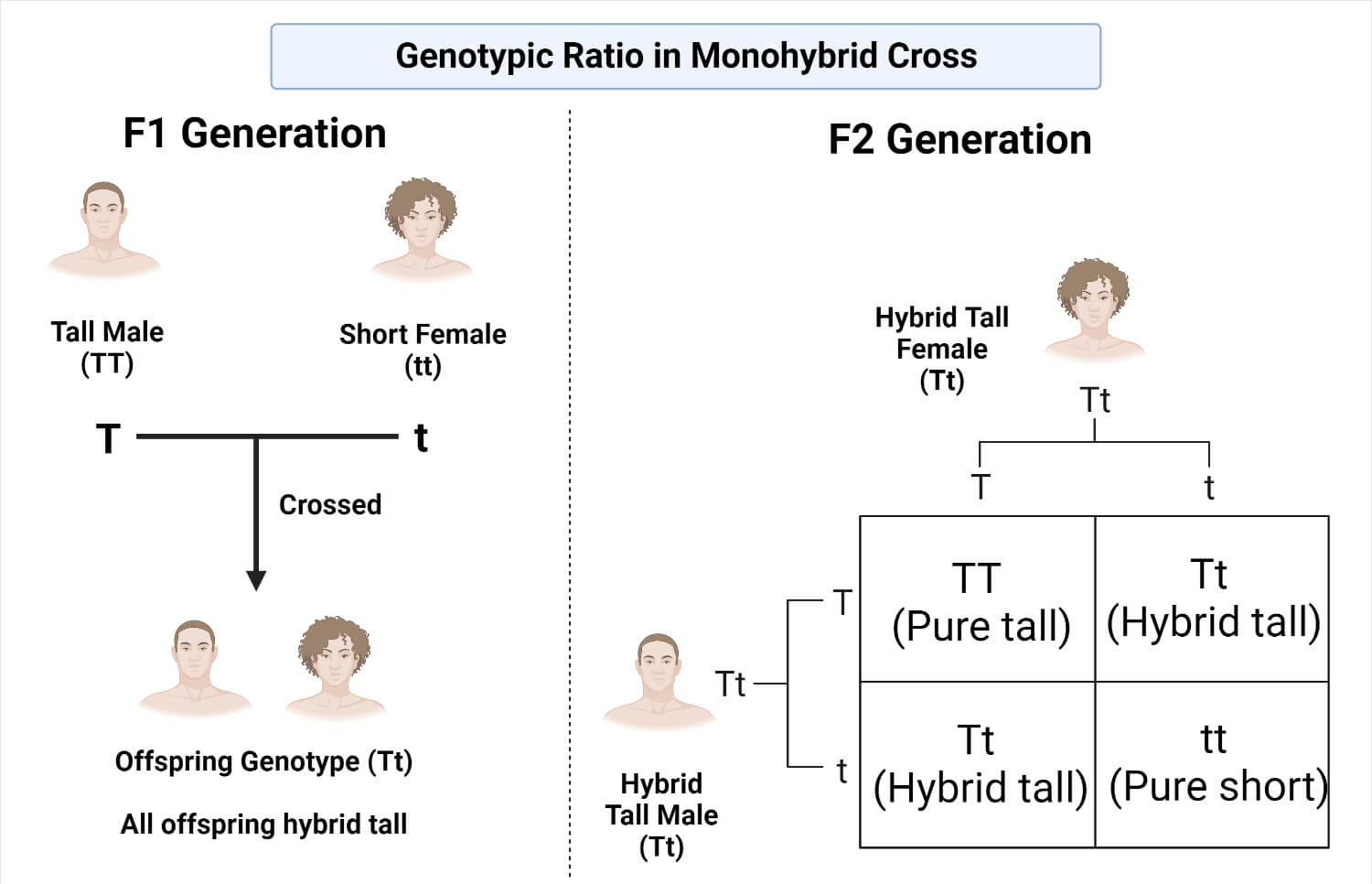
Deviation from Mendelian Ratio in Monohybrid Crosses A typical monohybrid cross as per Mendelian observation should show a phenotypic ratio of 3 1 in F2 generation But there are certain exceptions where one may find a deviation from the Mendelian ratio Feb 8 2025 nbsp 0183 32 When these F1 individuals are crossed the F2 generation exhibits a phenotypic ratio of 9 3 3 1 This ratio emerges from the combination of two independent monohybrid ratios 3 1 for each trait illustrating the independent assortment of alleles
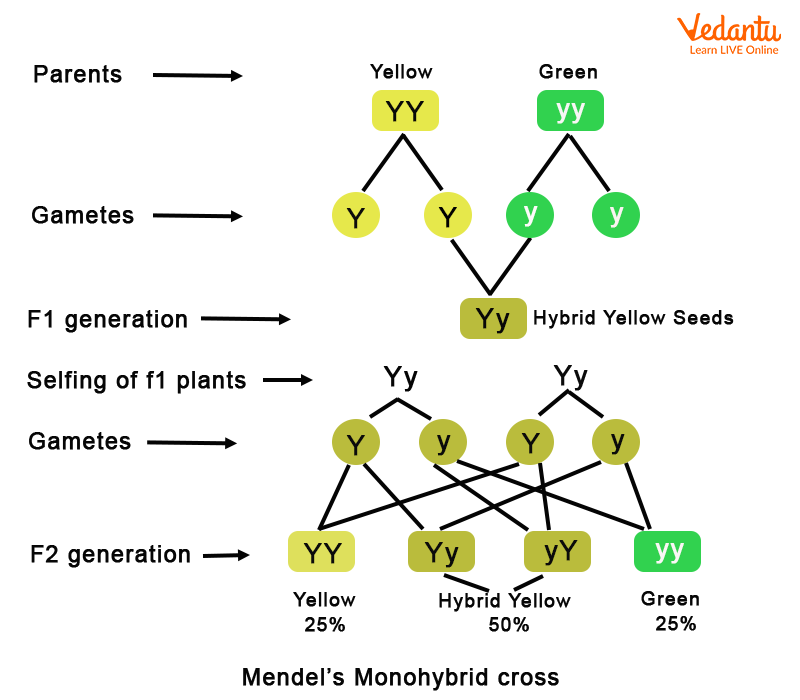
Aug 3 2023 nbsp 0183 32 Phenotypic Ratio in Monohybrid Cross The phenotypes in the second filial generation are tall three TT Tt Tt and short Only one tt So the phenotypic ratio of short and tall will be 3 1 respectively 10 2 1 Calculate and predict the genotypic and phenotypic ratio of offspring of dihybrid crosses involving unlinked autosomal genes A dihybrid cross determines the allele combinations of offspring for two particular genes that are unlinked not on the same chromosome
More picture related to The Phenotypic Ratios Of Monohybrid And Dihybrid Crosses Are Altered By

Difference Between Monohybrid And Dihybrid With Examples
https://www.pw.live/exams/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Difference-Between-Monohybrid-And-Dihybrid-jpg.webp

Called Dihybrid Cross Phenotypic Monohybrid Ratio In F2 Generation Is 3
https://static-images.findfilo.com/classroom/1677311236407_ntphqdxm_2486438.jpg

Monohybrid Vs Dihybrid Crosses Mr Smith Lecture Notes Biology
https://static.docsity.com/documents_first_pages/2022/09/27/d043ff29916aaabe5b0aa6098ee232be.png
Sep 21 2024 nbsp 0183 32 The phenotypic ratio observed in the F2 generation from a dihybrid cross is typically 9 3 3 1 showcasing the varied combinations of traits that can occur Understanding dihybrid crosses is not only beneficial for grasping the Monohybrid Dihybrid and Trihybrid Crosses Shading in each Punnett Square represents matching phenotypes assuming complete dominance and independant assortment of genes
Oct 16 2023 nbsp 0183 32 Monohybrid cross involves two alleles one from each parent for a single gene A Dihybrid cross involves four alleles two from each parent for two different genes Produces offspring with two possible phenotypes homozygous dominant and heterozygous Jan 30 2025 nbsp 0183 32 Monohybrid Cross A monohybrid cross involves one trait It s a simple way to study inheritance This cross helps find the phenotypic ratio for a single trait Consider a trait where A is dominant and a is recessive The possible combinations are AA dominant trait Aa dominant trait aa recessive trait

Difference Between Dihybrid Cross And Monohybrid Cross
https://st.adda247.com/https://www.careerpower.in/blog/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2023/10/13142658/difference-between-dihybrid-and-monohybrid-cross-1.png
Mendelian Ratio Learn Important Terms And Concepts
https://www.vedantu.com/seo/content-images/e8598a80-b323-4b30-bffe-81e90f8dd316.png
The Phenotypic Ratios Of Monohybrid And Dihybrid Crosses Are Altered By - Monohybrid Dihybrid Cross Ratio amp Mendelian laws Aim Experiments on monohybrid dihybrid cross ratio and deducing the applicability of Mendelian laws three examples of each ratio