Series Circuit Formula For Power Ohm s Law is a formula used to calculate the relationship between voltage current and resistance in an electrical circuit as shown below By knowing any two values of the Voltage Current or
The total power in a series circuit is equal to the SUM of the power dissipated by the individual resistors Total power PT is defined as PT P1 P2 P3 Pn As an example A series Apr 15 2025 nbsp 0183 32 A series circuit consists of a 15V power source a 20 resistor and a 30 resistor Calculate the total resistance current and voltage drop across each resistor R T 50 I
Series Circuit Formula For Power
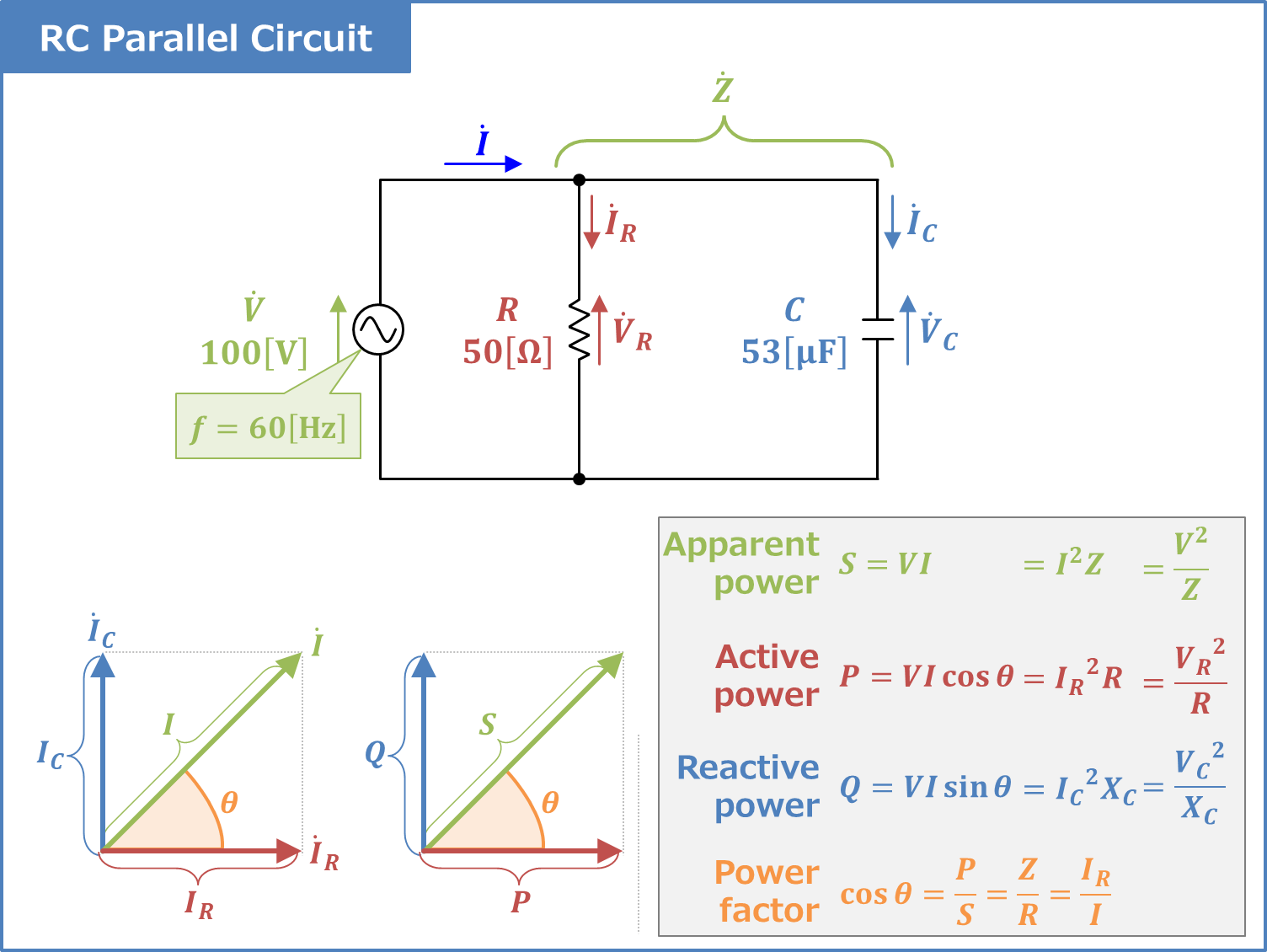
Series Circuit Formula For Power
https://electrical-information.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/RC-Parallel-Circuit-Power-factor-Active-Reactive-and-Apparent-power.png
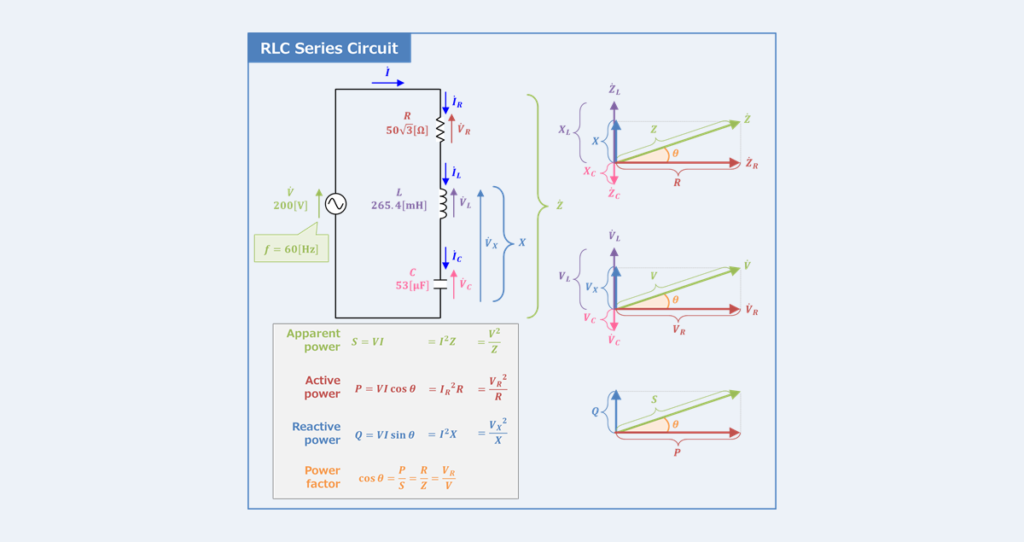
RLC Series Circuit Power Factor Active And Reactive Power
https://electrical-information.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/RLC-Series-Circuit-Power-Factor-Active-and-Reactive-Power.png
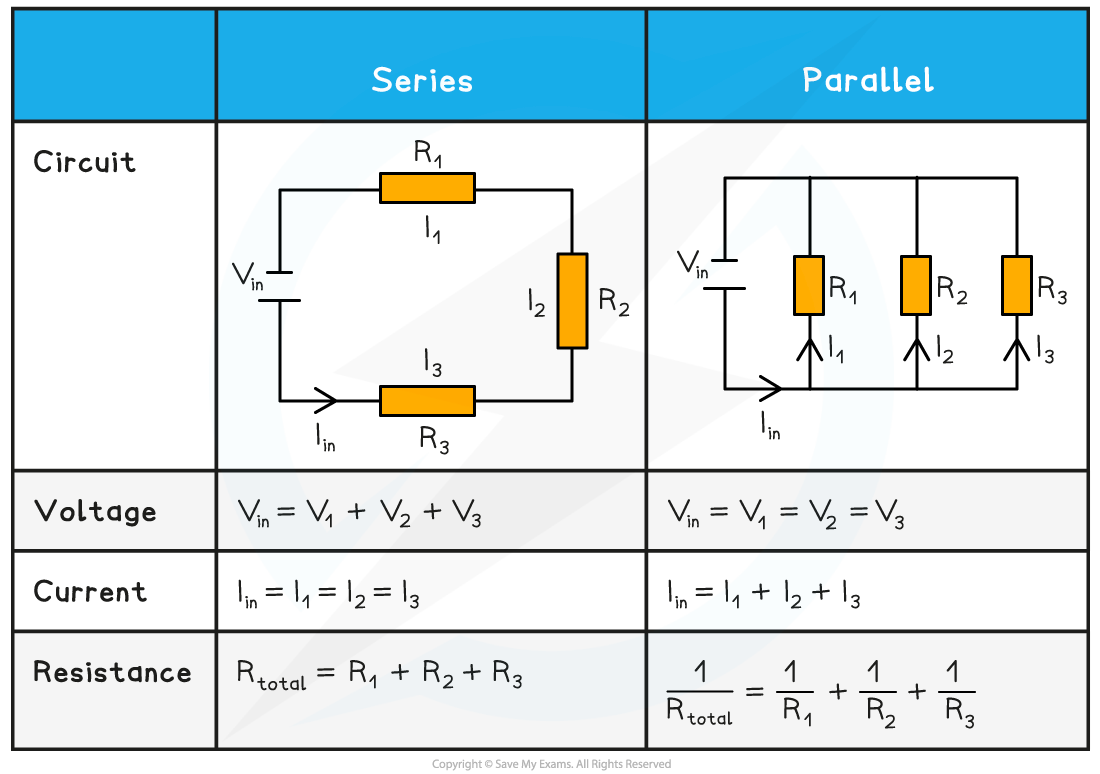
IB DP Physics SL 5 2 7 Series Parallel Circuits
https://oss.linstitute.net/wechatimg/2022/08/5.3.2-Series-_-Parallel-Circuits-Summary-Table_2-3.png
Mar 10 2025 nbsp 0183 32 Learn the formula for electrical power Power in an electrical circuit depends on two quantities current and voltage A higher current faster electrical charge transfers In a series circuit the total power is equal to the SUM of the power dissipated by the individual resistors Total power P T is equal to P T P 1 P 2 P 3 P n Example A series circuit
Nov 18 2024 nbsp 0183 32 The equivalent resistance R e for series and parallel circuits can be calculated using the following formula for power P I 2 R e Where I is the electric current flowing Dec 26 2021 nbsp 0183 32 The equation used to calculate power in each component is dependent on whether the circuit is in series or parallel For a series circuit use this equation to calculate the power P
More picture related to Series Circuit Formula For Power

Ohm s Law Vs Watts Law
https://hyperelectronic.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Ohms_Power_Law_Formula.png
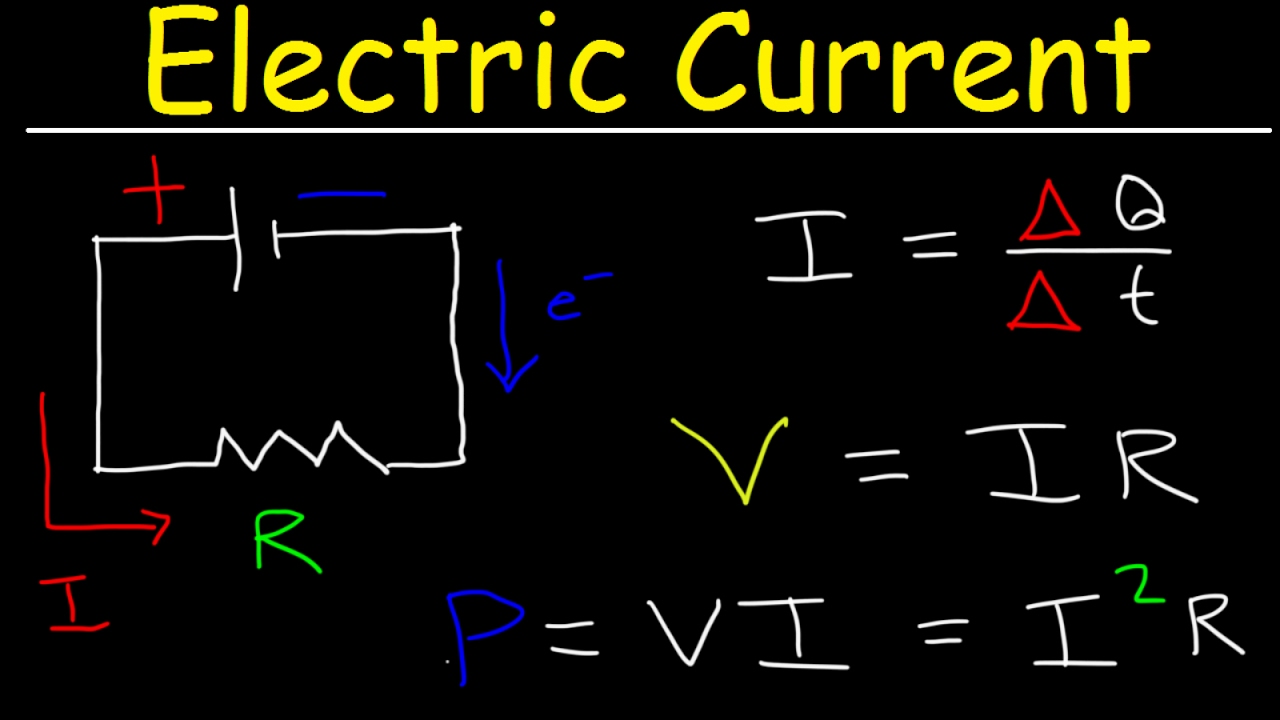
Electric Current Circuits Explained Ohm s Law Charge Power
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/r-SCyD7f_zI/maxresdefault.jpg
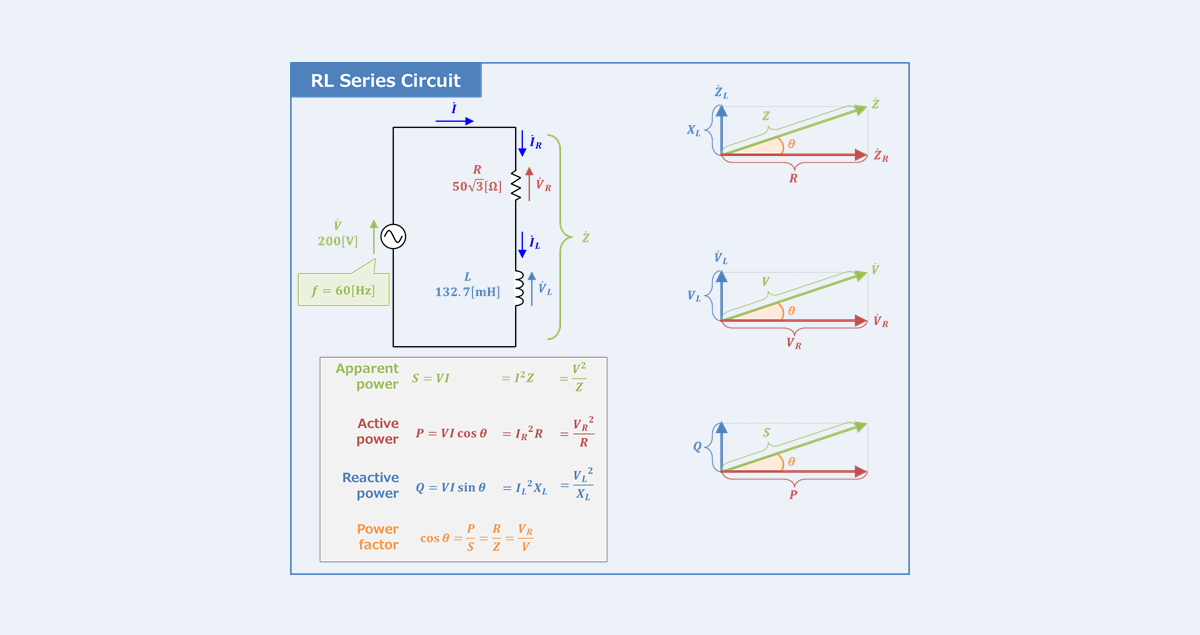
RL Series Circuit Power Factor Active And Reactive Power
https://electrical-information.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/RL-Series-Circuit-Power-Factor-Active-and-Reactive-Power.png
A circuit that contains pure resistance R ohms connected in series with a pure capacitor of capacitance C farads is known as RC Series Circuit A sinusoidal voltage is applied and By finding quot the magnitude V of the power supply voltage quot quot the magnitude I of the current flowing in the RC series circuit quot and quot the power factor cos theta of the RC series circuit quot
You can find below a table with every formula for the Power law and Ohm s law This table will be useful to solve problems and to understand examples Table 1 Ohm s law and Power law Mar 8 2025 nbsp 0183 32 The power of a series circuit is calculated by summing the power dissipated by each individual resistor in the circuit Here s a breakdown of how to calculate the total power P T in
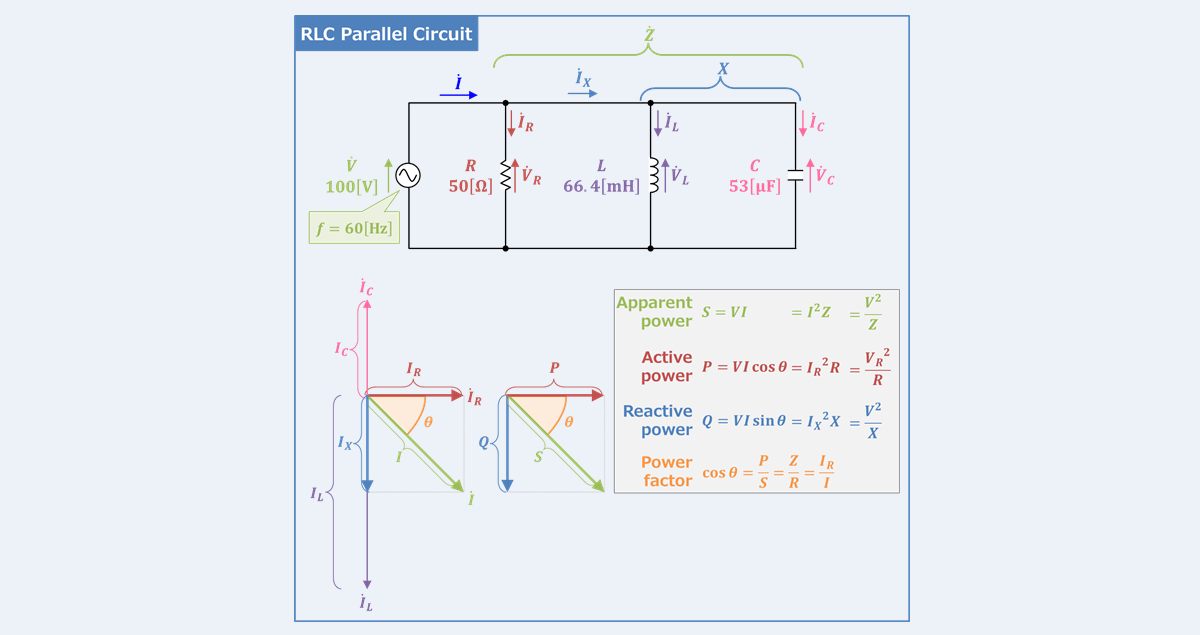
RLC Parallel Circuit Power Factor Active And Reactive Power
https://electrical-information.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/RLC-Parallel-Circuit-Power-Factor-Active-and-Reactive-Power.png
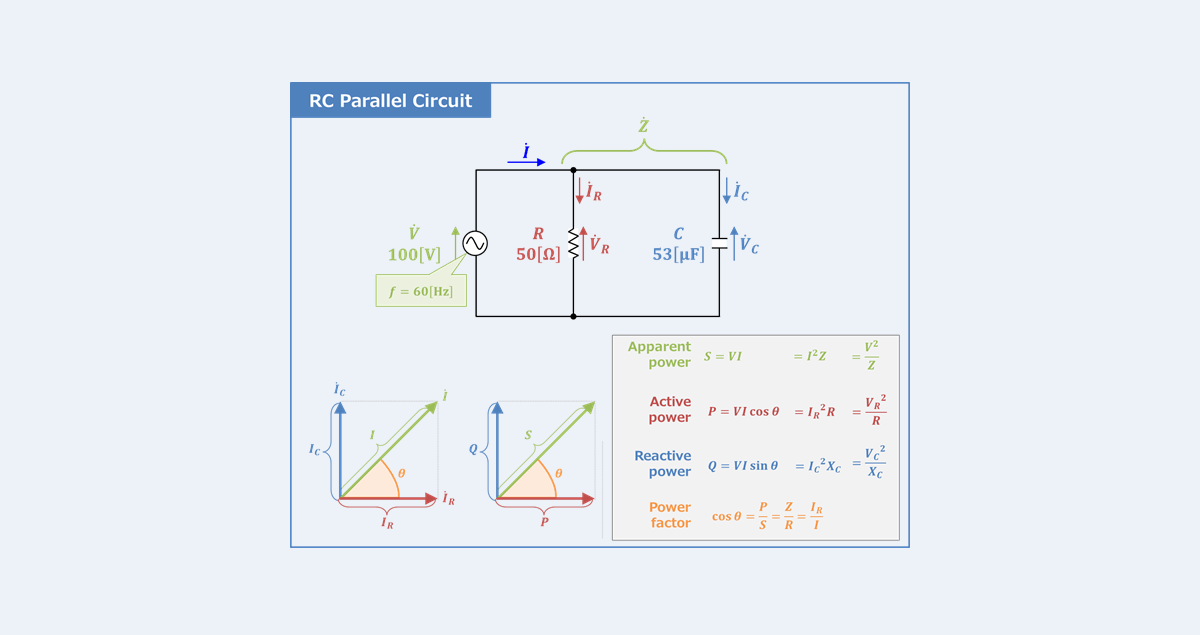
RC Parallel Circuit Power Factor Active And Reactive Power
https://electrical-information.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/RC-Parallel-Circuit-Power-Factor-Active-and-Reactive-Power.png
Series Circuit Formula For Power - Nov 18 2024 nbsp 0183 32 The equivalent resistance R e for series and parallel circuits can be calculated using the following formula for power P I 2 R e Where I is the electric current flowing