Series Circuit Example Problems Basic Steps To A Series Circuit Problem 1 See if you can do Ohm s Law V IR at any location in the circuit 2 See if you have current anywhere because that current will be the same everywhere following the series circuit rule below I T I 1 I 2 I 3 3 Check if you can do any of the other series circuit rules V T V 1 V 2 V
Series Parallel Circuit Example 1 Calculate the current drawn from the supply in the circuit shown in figure 2 a Solution Draw the equivalent circuit as in figure 2 b with R eq R 2 R 3 To compute equivalent resistance Series 1 Series Circuit circuit that has only one current path Dorling Kindersley Books Ex 1 Ammeter Meter that measures Current Reference Table Equations a IT I1 I2 I3 Total Current
Series Circuit Example Problems
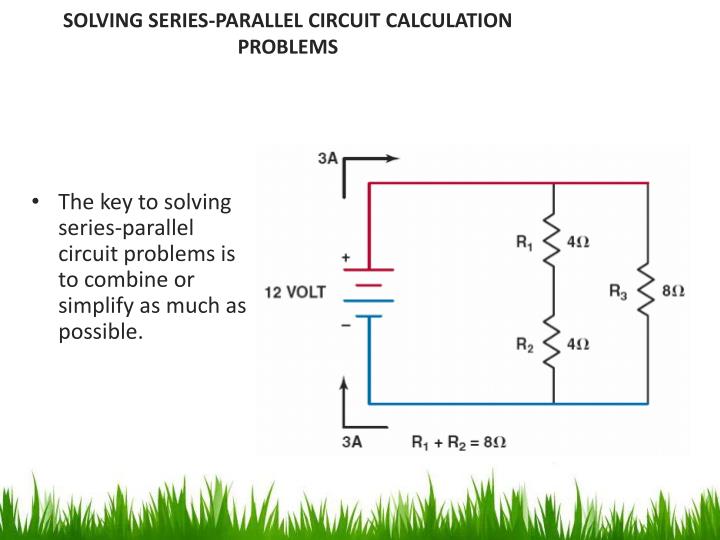
Series Circuit Example Problems
http://image3.slideserve.com/5446388/solving-series-parallel-circuit-calculation-problems-n.jpg

RLC Circuit Example Problem YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/x17ust61t7k/maxresdefault.jpg

Circuito Rlc
https://electricalacademia.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/RLC-Electrical-Network.gif
Jun 18 2021 nbsp 0183 32 Three cases of series RLC circuit Case 1 When X L gt X C i e X L X C is positive thus the phase angle is positive so the circuit behaves as an inductive circuit and has lagging power factor Worksheet Series Circuit Problems Episode 903 Name Remember that in a series circuit the current in every part of the circuit is the same adds up the voltage supplied by the battery is the voltage of the circuit and the voltage drops across each resistor is the same adds up to the total voltage
All About Circuits Series DC Circuits A set of open access problems with user activated answer keys The 27 problems all related to series circuits provide practice through multiple choice fill in the blanks and completion of data tables Jun 8 2024 nbsp 0183 32 A series circuit is the simplest type of circuit a single loop with no branching paths The electrical charge leaves the positive terminal of the power supply passes through each resistor or other components in turn then returns to the negative terminal
More picture related to Series Circuit Example Problems
Series Parallel Circuit Analysis Practice Problems Circuit 2 Wisc
https://www.wisc-online.com/images/learningobjectmetaimage/13162

Current Division Example Problem 2 Parallel Resistors YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/uxSHP0LaYFc/maxresdefault.jpg

AC Circuits Series Parallel RLC Example Problems YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/h3QCxHRkpg4/maxresdefault.jpg
Relate the voltage of a source to the voltage drops of individual resistors in a series circuit and relate the equivalent resistance to the individual resistor s resistance values Includes 8 problems Problem Set EC10 Series Circuits 2 Question The current flowing in a circuit containing four resistors connected in series is I 1 0A The potential drops across the first second and third resistors are respectively V 5V V 8V and V 7V The equivalent resistance of the circuit is R 30 Figure 2 Example Problem Resistors in series
[desc-10] [desc-11]
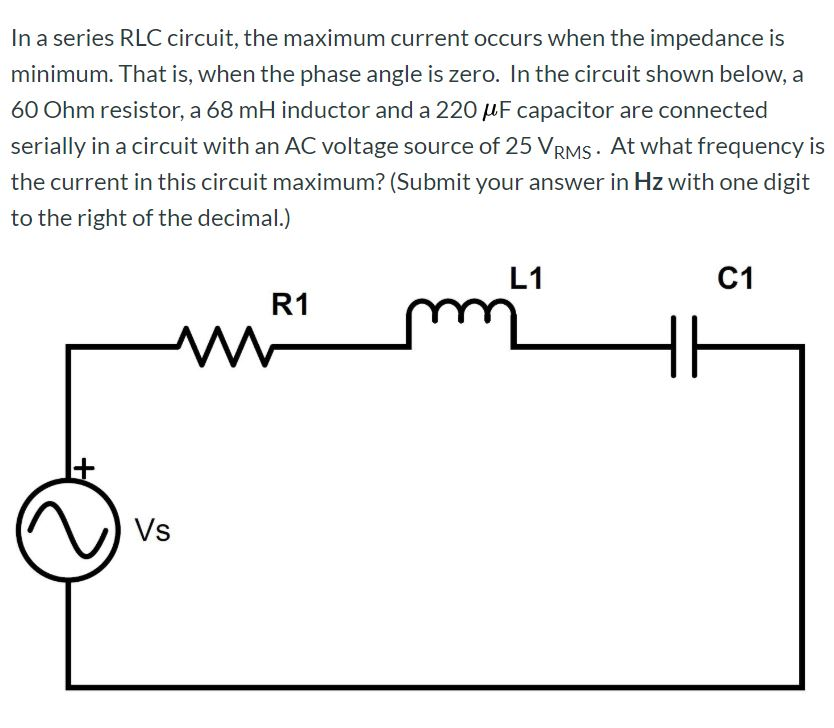
Solved In A Series RLC Circuit The Maximum Current Occurs Chegg
https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/141/14174691-8001-4b13-8b61-3ce0a77e6bd0/phpDx7NiW.png

How To Solve A Series Circuit 3 Steps with Pictures
http://www.wikihow.com/images/9/95/Solve-a-Series-Circuit-Step-3Bullet5.jpg
Series Circuit Example Problems - Worksheet Series Circuit Problems Episode 903 Name Remember that in a series circuit the current in every part of the circuit is the same adds up the voltage supplied by the battery is the voltage of the circuit and the voltage drops across each resistor is the same adds up to the total voltage
