How Does Lack Of Exercise Cause Coronary Heart Disease Jul 6 1999 nbsp 0183 32 In this report 9 it is stated that regular physical activity or cardiorespiratory fitness decreases the risk of cardiovascular disease mortality in general and of coronary heart disease in particular
Apr 20 2020 nbsp 0183 32 Physical activity and exercise training are effective strategies for reducing the risk of cardiovascular events but multiple studies have reported an increased prevalence of coronary atherosclerosis usually measured as coronary artery calcification among athletes who are middle aged and older You are less likely to develop coronary heart disease This is even if you smoke drink alcohol or don t have a healthy diet People of size greatly reduce their risk for disease when they get regular physical activity
How Does Lack Of Exercise Cause Coronary Heart Disease

How Does Lack Of Exercise Cause Coronary Heart Disease
https://myheart.net/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/CADinfographic-1.jpg

Exercise In Heart Disease MyHeart
https://myheart.net/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/Exercise-in-Heart-Disease.jpg

Benefits Of Physical Activity Physiopedia
https://www.physio-pedia.com/images/thumb/7/71/Health-benefits-of-physical-activity.png/900px-Health-benefits-of-physical-activity.png
In addition to reducing mortality exercise is associated with reduced incidence of coronary artery disease CAD and myocardial infarction MI 45 46 47 reduced risk of developing heart failure and reduced burden of arrhythmia Evidence regarding health benefits of physical activity is overwhelming and plays a critical role in both the primary and secondary prevention of coronary artery disease CAD Epidemiological investigations show approximately half the incidence of CAD in
Jun 24 2016 nbsp 0183 32 Physical activity PA is an independent and protective risk factor associated with reduced cardiovascular CV morbidity and mortality odds ratio 0 86 p lt 0 0001 and inactivity accounts for 12 2 of the population attributable risk for acute myocardial infarction MI and 6 of coronary heart disease CHD case s with an estimated 0 68 yea According to the CDC primary prevention of overweight obesity would reduce risks for coronary heart disease T2D hypertension dyslipidemia stroke non alcoholic fatty liver disease gallbladder diseases sleep apnea and respiratory problems osteoarthritis gynecological problems abnormal menses infertility endometrial postmenopausal
More picture related to How Does Lack Of Exercise Cause Coronary Heart Disease
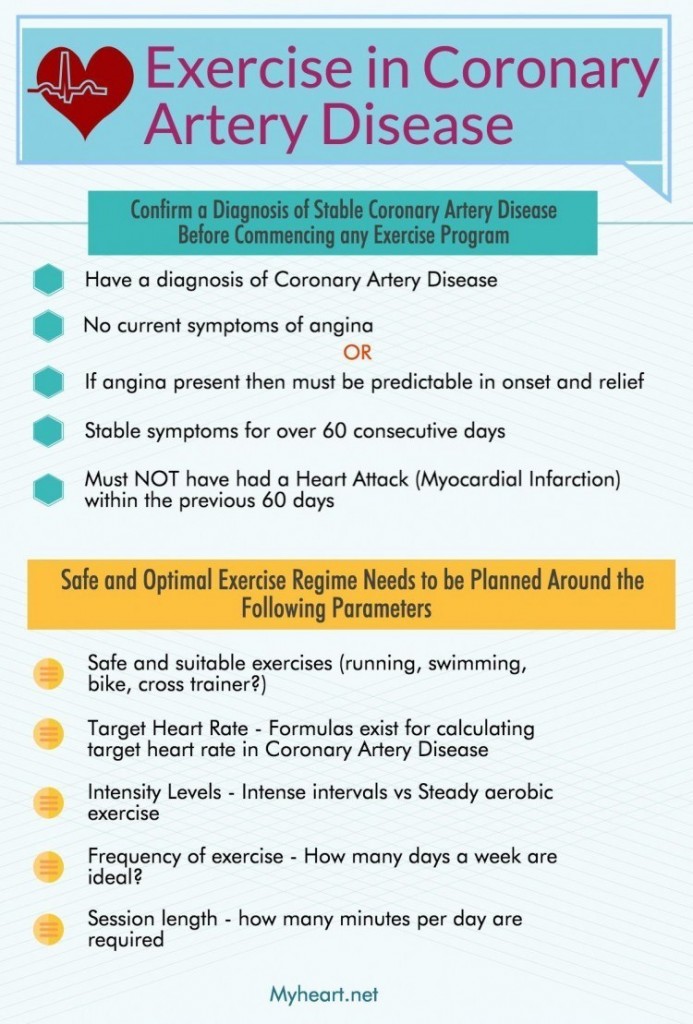
Exercise In Coronary Artery Disease MyHeart
https://myheart.net/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/Exercise-in-Coronary-Artery-Disease-693x1024.jpg

Kegel Exercises Healthcommunities Provider Services
https://www.healthcommunitiesproviderservices.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/kegel-for-men-iStock-1187114204.jpg

Cardiac Diet What It Is Foods To Consume Foods To Avoid Osmosis
https://d16qt3wv6xm098.cloudfront.net/X1zOlnC1RCSx4zi4w3JnBKR4QiK7gfuf/_.png
Reduce blood pressure and cholesterol which lowers your risk of getting heart and circulatory diseases like heart attacks strokes and vascular dementia reduce feelings of stress Should I exercise It s normal to worry whether you should exercise if you ve got a heart problem What are the consequences of physical inactivity for cardiovascular disease CVD Regular physical activity reduces the risk of dying prematurely from CVD It also helps prevent the development of diabetes helps maintain weight loss and reduces hypertension which are all independent risk factors for CVD
[desc-10] [desc-11]

Consequences Of Physical Inactivity In Teenagers Physical Activity In
https://physicalactivityteens.weebly.com/uploads/2/7/5/9/27594241/1020696_orig.jpg

Heart Stroke Vascular Diseases Statistics
https://www.australiawidefirstaid.com.au/media-library/infographic-on-heart-stroke-and-vascular-diseases-900w.jpg
How Does Lack Of Exercise Cause Coronary Heart Disease - In addition to reducing mortality exercise is associated with reduced incidence of coronary artery disease CAD and myocardial infarction MI 45 46 47 reduced risk of developing heart failure and reduced burden of arrhythmia