How Does Depression Affect The Brain Aug 24 2024 nbsp 0183 32 Depression is more than feeling down It may physically change your brain This can affect how you think feel and act Experts aren t sure what causes these changes They think genetics
Oct 9 2023 nbsp 0183 32 Having depression may correlate with certain brain changes including reduced gray matter neurotransmitter disruptions and inflammation People with depression may also experience Nov 1 2023 nbsp 0183 32 Depression while often thought of for its emotional symptoms has the potential to affect the physical structure of the brain Physical changes may range from inflammation to actual
How Does Depression Affect The Brain

How Does Depression Affect The Brain
http://depressedbrains.weebly.com/uploads/2/8/8/2/28824753/4888768_orig.jpg
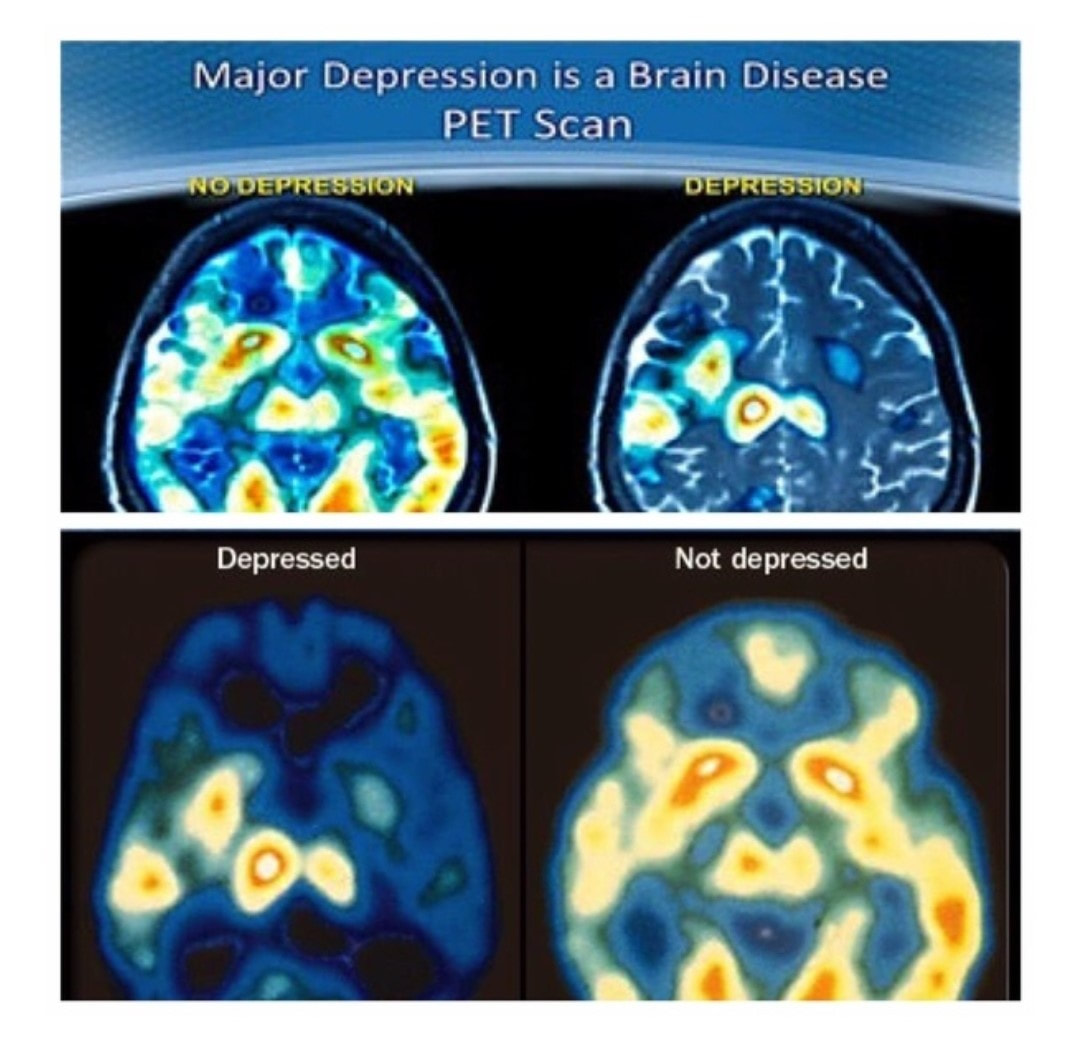
DEPRESSION
https://breakthesilencearoundmentalhealth.weebly.com/uploads/1/3/3/7/133785048/img-20200718-162201_orig.jpg

Quotes Depression Therapy QuotesGram
https://cdn.quotesgram.com/img/28/11/1185139449-img_img_9780781773164_depression_chart.jpg
Jul 11 2024 nbsp 0183 32 Depression s impact on the brain is multifaceted involving alterations in neurotransmitter function structural changes in key brain regions and disruptions to neural plasticity Understanding these neurobiological underpinnings is crucial for developing more effective treatments and improving outcomes for individuals with depression Numerous studies that focused on gray and white matter have found significant brain region alterations in major depressive disorder patients such as in the frontal lobe hippocampus temporal lobe thalamus striatum and amygdala The results are inconsistent and controversial because of the different demographic and clinical characteristics
Sep 22 2021 nbsp 0183 32 Researchers have been able to determine that depression directly impacts multiple areas of the brain most of which are affected by a loss of gray matter volume GMV Gray matter is a type of brain material that s dense with cells and needed for strong brain activity In this review evidence from neuroimaging neuropsychiatric and brain stimulations studies are explored to answer the question regarding the localization of depression in the brain Neuroimaging studies indicate that although many regions of the brain have been repeatedly implicated in the pathophysiology of depression not many consistent
More picture related to How Does Depression Affect The Brain
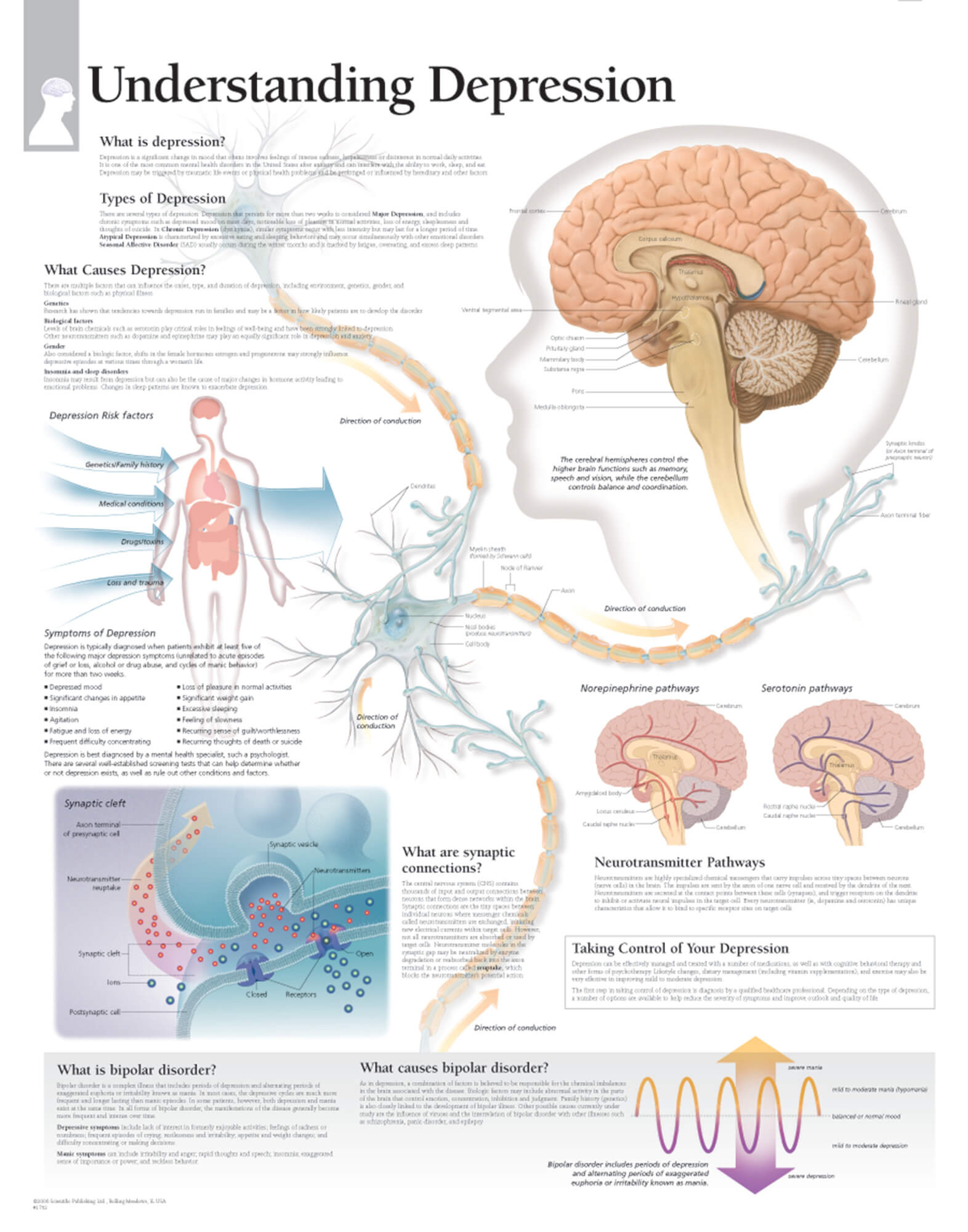
Understanding Depression Scientific Publishing
https://www.scientificpublishing.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/understanding-depression-anatomical-wall-chart.jpg

Depression Brain Diagram
https://psychscenehub.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/Deconstructing-depression-2.png

Depression Brain Diagram
https://image.slideserve.com/756735/depression-and-the-brain-l.jpg
Jun 17 2021 nbsp 0183 32 What we know right now is that on a chemical level depression involves neurotransmitters which can be thought of as the messengers that carry signals between brain cells or neurons Oct 25 2022 nbsp 0183 32 One of the main questions that directs clinical studies about affective disorders such as depression is how does depression affect the brain According to research depression affects brain plasticity which is described as the ability of the vast network of nerves in the brain to grow and reorganize in response to internal or external
[desc-10] [desc-11]

Depression Brain Diagram
https://img.haikudeck.com/mg/oaaWkAKa76_1446153223253.jpg
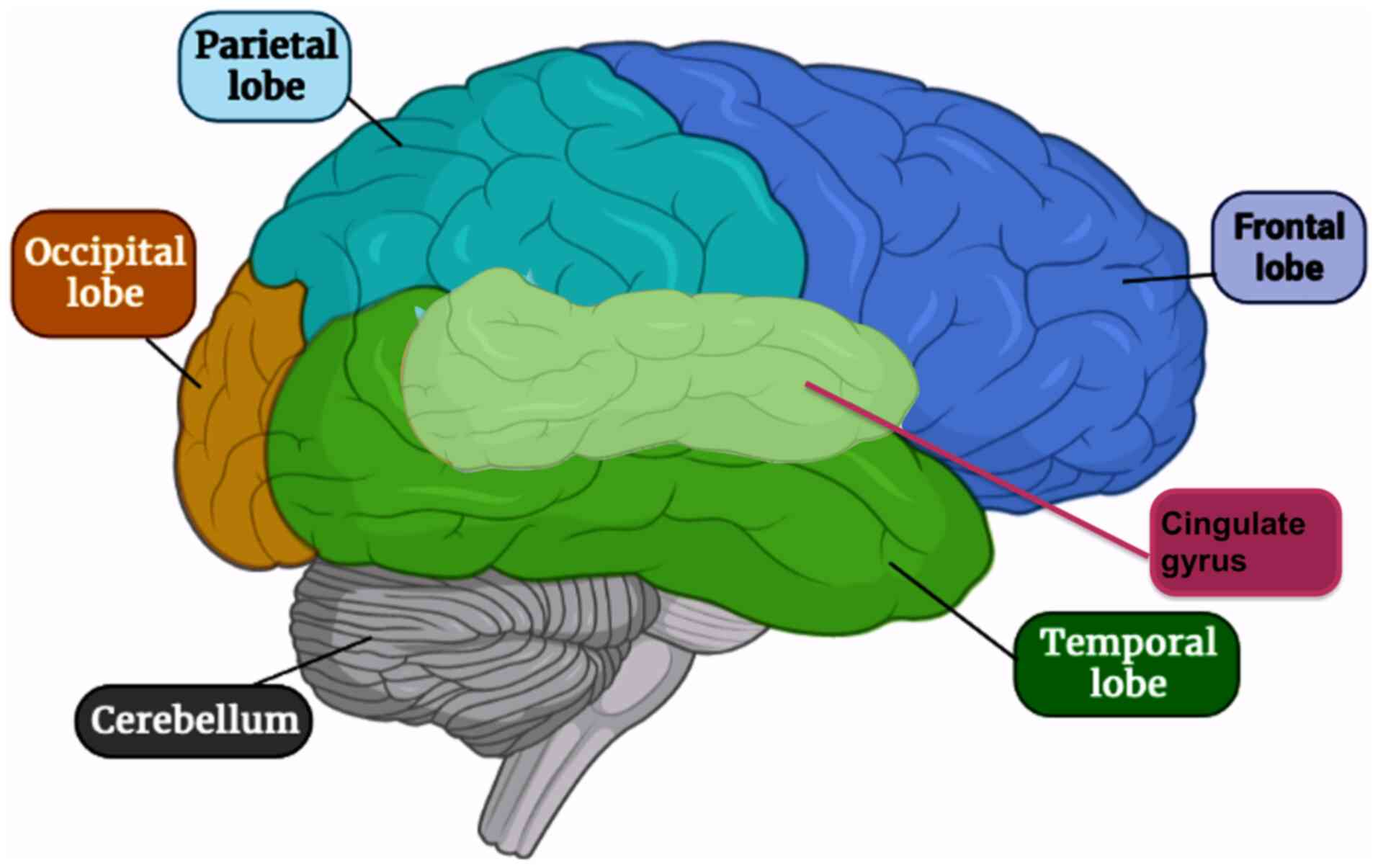
Depression Brain Map
https://www.spandidos-publications.com/article_images/mmr/24/6/mmr-24-06-12479-g00.jpg
How Does Depression Affect The Brain - Numerous studies that focused on gray and white matter have found significant brain region alterations in major depressive disorder patients such as in the frontal lobe hippocampus temporal lobe thalamus striatum and amygdala The results are inconsistent and controversial because of the different demographic and clinical characteristics