Explain Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure And Copy Equation What is Dalton s Law Dalton s law of partial pressures is a gas law which states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures exerted by each individual gas in the mixture
Let s take a closer look at pressure from a molecular perspective and learn how Dalton s Law helps us calculate total and partial pressures for mixtures of gases In this article we will be May 6 2019 nbsp 0183 32 In 1801 Dalton formulated a law now known as Dalton s law of partial pressures which states that The total pressure of a mixture of gases is just the sum of the pressures that
Explain Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure And Copy Equation

Explain Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure And Copy Equation
https://sciencenotes.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Daltons-Law-of-Partial-Pressure.png
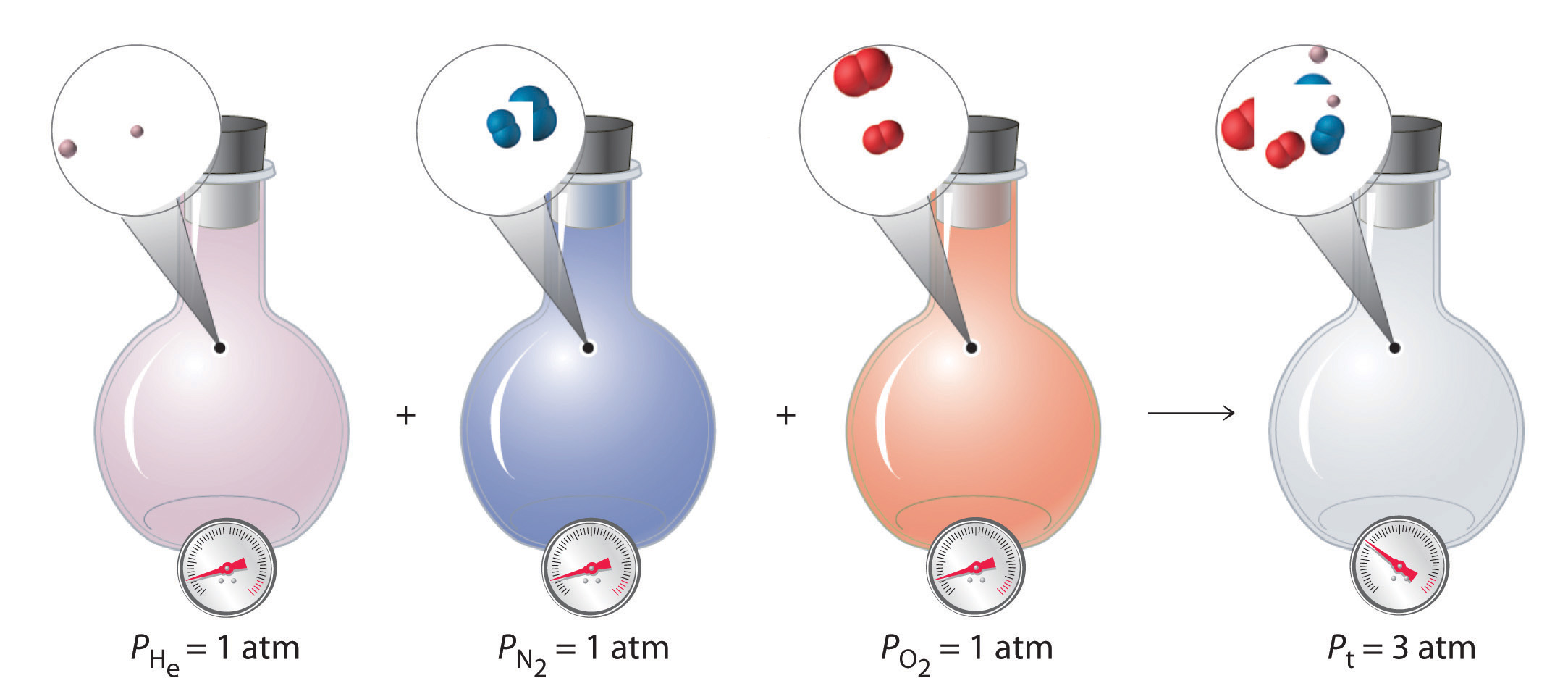
Dalton s Law
https://users.highland.edu/~jsullivan/genchem/section_12/afc389d4e21d6ac749d2d2f87e9204cd.jpg

Dalton s Law Of Partial Pressures Explained YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/qh1JRtPhivc/maxresdefault.jpg
Understand Dalton s Law of Partial Pressure its formula and how it explains gas mixtures Explore partial pressure mole fraction derivations and practical applications Answer The dalton s law of partial pressure states that when there is a mixture of inactive gases there is no reaction between them the total pressure applied is equal to the sum of the partial
Feb 8 2025 nbsp 0183 32 The partial pressure of each gas in a mixture is proportional to its mole fraction and can be computed using the following relation Dalton s Law offers view that help to clearly understand and correctly predict what will Feb 22 2025 nbsp 0183 32 Dalton s Law of Partial Pressure is a fundamental principle in understanding how gases behave when they are mixed It provides a simple way to calculate the total pressure in
More picture related to Explain Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure And Copy Equation
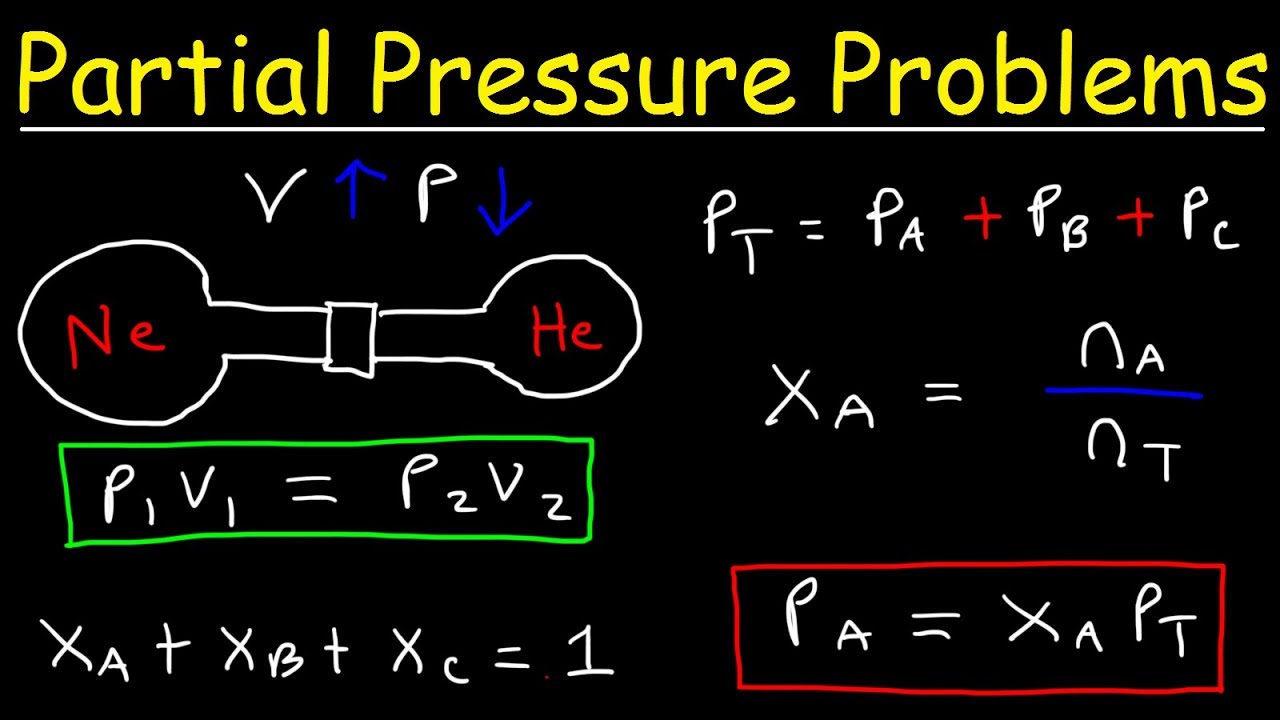
Dalton s Law Of Partial Pressure Problems Mole Fraction Chemistry Gas
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/J7YRwU7IV8Q/maxresdefault.jpg

DALTON S LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURES STATES OF MATTER 17 YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/rNxDFS_-wYU/maxresdefault.jpg

Dalton s Law chemical physics example Information Poster With
https://i.pinimg.com/originals/5c/31/89/5c31894d985e68fa6bcb0e0a204f99ef.jpg
Nov 21 2023 nbsp 0183 32 Partial pressure is calculated by setting the total pressure equal to the partial pressures The formula is PT P1 P2 P3 PN Where PT is the total pressure and all other Partial pressure of such gases is calculated by using the following mathematical expression of Dalton s law of partial pressure P total P gas P water vapour P gas P total P water vapour The partial pressure of water vapour in gases
Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures states that the total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases P total P 1 P 2 P 3 Dalton s law of partial pressure states that in a mixture of two or more non reacting gases the sum of the partial pressures of each gas is equal to the overall pressure of the gas mixture

Henry s Law Partial Pressure Gas Solubility And Mole Fraction YouTube
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/SpQGxcYl0ws/maxresdefault.jpg

Physiology Glossary Partial Pressures Ditki Medical Biological
https://d1j63owfs0b5j3.cloudfront.net/term/images/697-1650305693728.png
Explain Dalton S Law Of Partial Pressure And Copy Equation - Dalton s Law of Partial Pressures Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases Behaviour of Real Gases Deviation from Ideal Gas Behaviour Liquefaction of Gases Vapour Pressure Surface Tension